Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations (PAVMs) are abnormal communications between the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein without an intervening capillary system. PAVMs are most commonly associated with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, a rare autosomal dominant disorder [1]. Acquired PAVMs occur in patients with chronic liver disease, history of cardiosurgical procedures or thoracic trauma, metastatic thyroid cancer or Fanconi syndrome [2]. The presenting symptoms including dyspnea, hypoxemia and chest pain result from right-to-left shunt, cardiac volume overload and destruction of lung parenchyma. Establishing the final diagnosis is difficult and requires multi-disciplinary workup. Traditional surgical management of PAVM has been gradually replaced by minimally invasive embolotherapy which became a gold standard of treatment [3].
We hereby present the case of a patient with two PAVMs resulting in worsening dyspnea and cyanosis successfully treated by endovascular embolization.
A 32-year-old man with two clinically known PAVMs (one significantly bigger in the left lung and one smaller in the right lung (Figure 1 A)) treated for over 10 years with home oxygen therapy was admitted to the Department of Pulmonology. Because of the congenital character of the disease he was adopted to low oxygen saturation, however, over few weeks he reported increasing weakness and 2 episodes of loss of consciousness. Baseline results: oxygen saturation – 78%, PaO2 – 42 mm Hg, PaCO2 – 35 mm Hg, pH – 7.45. Due to severe dyspnea and clinical deterioration, he was referred to the Department of Interventional Radiology for an endovascular procedure. In local anesthesia, the femoral vein access was obtained, left pulmonary vein catheterized and PAVM depicted (Figure 1 B). The embolization of the feeding arteries, AVM nidus and AVM-associated aneurysms was consecutively preformed with coils (Nester and MReye, Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA) and 10 mm Amplatzer Vascular Plug (St. Jude Medical, MN, USA). A control contrast injection showed complete elimination of PAVM of the left lung (Figure 1 C). Immediate improvement of the patient’s condition was observed. Oxygen saturation measured directly after the procedure was 95%. Arterial-blood gas values 24 h post-embolization confirmed the improvement of oxygenation – PaO2 – 77 mm Hg, PaCO2 – 31 mm Hg, pH – 7.40.
Figure 1
A – Chest CT-angio depicting pulmonary fistulas – the bigger one (arrow) between the left pulmonary artery (triangle) and left pulmonary vein (circle) and the smaller one (star) on the right side. B – Selective angiography of the lower segmental branches of the left pulmonary artery. Visible huge pulmonary AVM with AVM-associated aneurysms (stars) of the branches of the left pulmonary vein. C – Post-procedural control angiography confirming complete coil-embolization of the PAVM of the left lung (arrow). D – Control angiography after the secondary procedure from the vascular sheath located in the right pulmonary artery trunk (star). Visible complete coil-embolization of the PAVM (arrow)
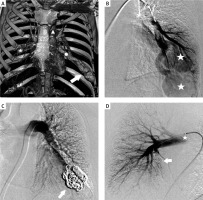
The patient was discharged from the hospital 2 days after the procedure in good clinical condition. Smaller PAVM of the right lung was successfully treated with coil embolization 3 months after the primary procedure (Figure 1 D).
This case report demonstrates that the awareness of possible treatment of rare diseases is insufficient both in the general public and among healthcare professionals. This young individual spent over 10 years from the first CT-angio examination to the final procedure under medical supervision treated only with home oxygen therapy. This led to gradual deterioration of his condition and resignation from active lifestyle. After a decade of conservative treatment he incidentally came across a similar case successfully embolized in our Department. In specialized centers the outcome of embolotherapy of PAVM is very satisfactory, with excellent clinical results and acceptable recurrence and complication rates [4]. However, the knowledge of treatment possibilities remains crucial in order to prevent life-threatening complications associated with PAVMs.







