Despite the advent of myosin inhibitors resulting in the growing role of pharmacotherapy, the treatment options for symptomatic patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) still include alcohol ablation of the interventricular septum (IVS) [1]. Precise identification of the target coronary artery branch is necessary to limit the muscle scarring to the region responsible for LVOTO. Typically, one of the proximal septal branches of the anterior descending artery proves appropriate but, in some cases, identifying the correct one requires sequential contrast administration to several neighboring branches [2, 3].
We present the applicability of fusion imaging with the Heart Navigator system, allowing the transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) marker to be superimposed on the angiographic image for precise selection of the ablation vessel.
First, the part of the proximal segment of the IVS along which the greatest color Doppler flow turbulence occurs is identified by TEE biplanar imaging. This area is marked with a marker (Figure 1 A), which is simultaneously displayed on the corresponding angiographic image (Figure 1 B). The septal branch pointing towards the marker is then selectively catheterized using an over-the-wire balloon catheter with a diameter appropriate for the vessel size (in the present case, a 2 mm balloon catheter). After inflating the balloon, angiographic contrast agent is injected through the central lumen of the balloon catheter to confirm the proper identification of the vessel (opacification of the target IVS area is also visible on TEE). Finally, a suitable amount of absolute alcohol is introduced into the central lumen of the balloon catheter to perform myocardial ablation. Figures 1 C and D show the coronarography before and after the procedure.
Figure 1
A – TEE of proximal segment of the IVS along which the greatest color Doppler flow turbulence occurs, B – marker from TEE simultaneously displayed on the corresponding angiographic image, C – coronarography before procedure, D – coronarography after procedure
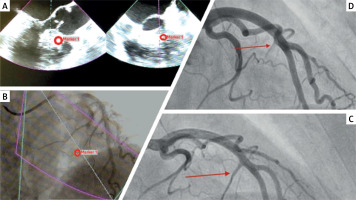
The presented method of fusion imaging allows one to conveniently combine, in one real-time image, the echocardiographic identification of the IVS subsegment responsible for LVOTO with the angiographic selection of the delivering septal branch.








