Introduction
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a common allergic skin disease characterized by recurring pruritic skin eruptions that last for 6 weeks or more, without any specific external stimuli or triggers. CSU is more common in females, especially those aged 30–50 [1]. The typical clinical manifestations of CSU are recurring skin itching and erythematous rashes, which can occur in various parts of the body with varying sizes and shapes. CSU can also present with oedema and deep tissue swelling, and in severe cases, it can affect the function of organs such as respiration and circulation. Pain and burning sensation are also common symptoms of CSU [2, 3]. The pathogenesis of CSU is not yet fully understood, but research suggests that it may be related to autoimmune reactions, inflammatory responses, and genetic factors [4].
Serum inflammatory cytokines (SICs) are the body’s response to various stimuli, and they participate in regulating the proliferation, differentiation, and function of immune cells, as well as modulating the process of inflammation [5]. Many studies have found [6, 7] that the expression levels of various inflammatory factors are elevated in the bodies of CSU patients, and the expression levels of these inflammatory factors are closely related to the severity of the disease. The inflammatory response plays an important role in the pathogenesis of CSU. The production of inflammatory factors can occur through various pathways, including immune cell activation, cell death, and cytokine induction. These inflammatory factors can cause inflammation in skin tissue, resulting in symptoms such as vasodilation, tissue oedema, and skin itching [8]. In addition, CSU patients’ serum can also detect some autoantibodies, such as anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody and anti-cell membrane antibody, and the production of these autoantibodies is also closely related to the inflammatory response [9, 10]. For CSU, antihistamines are currently the main treatment method [11]. However, for some patients, antihistamines may not alleviate their symptoms very well. Therefore, it is very important to search for other effective treatment methods. Some studies have found [12, 13] that targeting specific inflammatory factors for treatment may be an effective approach. Therefore, in-depth research on inflammatory factors in CSU patients can provide new ideas and methods for the treatment of this disease.
Understanding the levels of SICs in CSU patients can aid doctors in selecting more effective treatment strategies. Several studies have found that using anti-inflammatory drugs can decrease SIC levels in patients, thereby alleviating symptoms and easing the disease [14, 15]. Therefore, understanding a patient’s SIC levels can guide doctors in selecting more accurate treatment plans and improve treatment effectiveness. Exploring the relationship between levels of SICs in CSU patients and the severity of the disease can better help understand its pathogenesis. Currently, the pathogenesis of CSU is not fully understood, but the increase in SICs is considered an important factor. In addition, exploring the relationship between SICs and disease severity can provide a basis for disease prognosis evaluation [16]. Currently, the prognosis evaluation for CSU is not perfect, and understanding a patient’s SIC levels may help evaluate their prognosis and provide a reference for doctors to develop more personalized treatment plans.
Material and methods
Research objects
114 patients with CSU admitted to the outpatient department of Jiaxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from April 2022 to July 2023 were selected as the study population and designated as the research group (Res group). Meanwhile, 100 healthy individuals who underwent physical examinations at the same hospital during the same period were randomly selected and designed as the Ctrl group. The patients with recent local or systemic infectious diseases, organic diseases, allergies such as asthma, atopic dermatitis, and autoimmune diseases were excluded. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jiaxing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and patients and their families were informed and willingly participated in the study by signing an informed consent form.
Criteria for enrolling relevant patients in this work were as follows: I. a clear diagnosis of CSU; II. presence of clinical symptoms such as skin itching and hives lasting for 6 weeks or more; III. age of 18 years or older; and IV. no use of antihistamines, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, or immunomodulators in the 3 weeks prior to the study.
Criteria for excluding the patients were as follows: I. significant liver or kidney dysfunction; II. concurrent systemic infectious diseases; III. concurrent other allergic or autoimmune diseases; IV. pregnant or lactating women; V. incomplete clinical data; and VI. inability to cooperate with the study due to various reasons.
Main reagents and instruments
The experimental reagents and instruments included enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits for leukotriene B4 (LTB4), leukotriene C4 (LTC4), interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-17 (IL-17), interleukin-31 (IL-31), and tumor necrosis factor-γ (TNF-γ) from Shanghai Yanjin Biological Technology Co., Ltd.; horseradish peroxidase (HPR) from Hubei Wede Li Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.; wash buffer from Shanghai Huzhen Industry Co., Ltd.; ultra-low temperature refrigerator from Shanghai Jianheng Instrument Co., Ltd.; high-speed centrifuge from Hunan Kaida Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.; and microplate reader from Beijing Sairui Fu Technology Co., Ltd.
Detection of SICs
The levels of LTB4, LTC4, IL-4, IL-17, IL-31, and TNF-γ were determined using ELISA kits (Shanghai Yenji Bioscience Co., Ltd). Before beginning the experiment, all reagents were taken out from the refrigerator and equilibrated to room temperature. Then, 50 μl of prepared standard was added to the corresponding standard wells, followed by the addition of 100 μl of horseradish peroxidase. Meanwhile, 50 μl of the test sample was placed in the corresponding sample wells, followed by the addition of 100 μl of horseradish peroxidase. The blank and control wells did not receive any sample. Then, the samples were subject to an incubation at 37°C for 60 min, covered with a sealing film, and gently shaken. Next, the wells were washed 5 times with wash buffer, and then 50 μl of substrate A and 50 μl of substrate B was added for a 15-min incubation at 37°C. After that, the reaction was stopped by adding 50 μl of stop solution. Finally, the optical density (OD) of each well was measured to be 450 nm within 15 min.
Evaluation criteria
The pruritus severity was evaluated using Visual Analog Scale (VAS) commonly, which ranged from 0 to 10 on different levels of intensity. This rating method usually required patients to mark the level of itchiness they currently experience on a line, with one end representing “no itch” and the other end representing “extremely severe itch”. The severity of pruritus was then evaluated by measuring the distance between the marked point and the starting point of the line. The severity of pruritus was classified into three categories: mild, moderate, and severe. Mild pruritus (1–3 points) was determined with tolerable itching, no scratch marks on the skin, and no influence on sleep. Moderate pruritus (4–6 points) was considered if there was noticeable itching, scratch marks on the skin, and mild sleep disturbances. Severe pruritus (7–10 points) was reflected by intolerable itching, still noticeable itching on the skin, and severe sleep disturbances.
The duration of pruritus was generally evaluated using a 3-level rating scale. A score of 0, 1, and 2 indicated a duration of less than 30 min, between 30 and 120 min, and longer than 120 min, respectively. This assessment was usually done by asking the patient about the duration of their current and previous symptoms.
Urticaria Activity Score (UAS) was utilized to assess the activity of chronic urticaria, which included the number of wheals and pruritus severity. It scored the number of wheals and pruritus severity in the past 7 days for patients with chronic urticaria. The number of wheals was graded into four levels, from none to severe, with 0–3 points, respectively; pruritus severity was also evaluated as four levels, from none to severe, with 0–3 points, respectively. The daily score ranged from 0 to 6, and the total score was obtained by adding up the scores for seven consecutive days, with a range of 0–42 days. Based on the total score, patients were classified into three groups: mild (0–14), moderate (15–28), and severe (29–42).
Furthermore, the Chronic Urticaria Quality of Life Questionnaire (CU-Q2oL) was frequently applied to assess the quality of life (QOL) in patients with CSU. It consisted of 23 questions covering various aspects, such as itching, sleep, daily activities, and psychological status. Each question was scored on a 5-point scale, where 1 indicated an extremely severe impact on QOL, and 5 indicated no impact on QOL. Based on the total score, patients can be categorised into three: mild impact (total score ≥ 76), moderate impact (50 ≤ total score < 76), and severe impact (total score < 50).
Statistical analysis
The data from the experiment were analysed using SPSS 20.0. Mean ± standard deviation was utilized to describe quantitative data. Independent sample t-tests or analysis of variance were employed for comparing normally distributed data, while non-parametric rank-based tests were applied for comparing the non-normally distributed data. Pearson’s correlation analysis (PCA) was adopted to examine the correlation between SICs and the severity of CSU, with α = 0.05 and p < 0.05 indicating a statistical significance.
Results
Clinical data of patients
As illustrated in Figure 1, the subjects in the Res and Ctrl groups exhibited a comparability in age, gender, and body mass index (BMI), with no obvious differences observed (p > 0.05).
Levels of SICs of patients in various groups
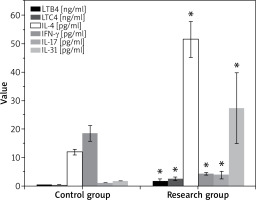
Figure 2 below compared the levels of LTB4, LTC4, IL-4, IL-17, IL-31, and TNF-γ of patients in various groups. It demonstrated that the patients in the Res group exhibited higher LTB4, LTC4, IL-4, IL-17, and IL-31 levels but lower TNF-γ levels compared to those in the Ctrl group, showing great differences with p < 0.05.
SICs of patients with different pruritus severities
As displayed in Table 1, pruritus severity of patients can be mild (n = 35), moderate (n = 54), and severe (n = 25). The Kruskal-Wallis test (KWT) was utilized to compare the differences in IL-4, IL-17, and IL-31 levels among the three groups. The results revealed obvious differences in them among patients with mild, moderate, and severe pruritus (p < 0.05).
Table 1
SICs of patients with different degrees of pruritus severity
| Indicators of SICs | Mild pruritus (n = 35) | Moderate pruritus (n = 54) | Severe pruritus (n = 25) | χ2 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTB4 [ng/ml] | 1.46 ±0.24 | 1.82 ±0.35 | 2.15 ±0.51 | 10.567 | 4.257 |
| LTC4 [ng/mll] | 2.15 ±0.35 | 2.67 ±0.57 | 3.11 ±1.03 | 9.245 | 5.029 |
| IL-4 [pg/ml] | 45.24 ±6.23* | 50.73 ±6.84* | 55.25 ±7.02* | 16.355 | < 0.05 |
| IL-17 [pg/ml] | 1.52 ±0.22* | 3.83 ±0.65* | 5.02 ±1.16* | 20.567 | < 0.05 |
| IL-31 [pg/ml] | 16.73 ±5.12* | 30.56 ±6.31* | 35.36 ±7.82* | 18.572 | < 0.05 |
| TNF-γ [pg/ml] | 6.53 ±0.67 | 5.72 ±0.43 | 4.56 ±0.38 | 8.458 | 3.631 |
SICs of patients with different durations of pruritus
The patients were grouped into three groups according to their duration of pruritus: < 30 min (n = 33), 30–120 min (n = 33), and > 120 min (n = 43 cases). The KWT was utilized for comparing the duration of pruritus of patients in different groups, and no visible difference was observed, showing p > 0.05. The specific values of relevant SICs were summarized in Table 2 below.
Table 2
SICs of patients with different durations of pruritus of patients
SICs of patients with different degrees of urticaria activity
The patients were grouped into three groups according to their degrees of urticaria activity: mild (n = 32), moderate (n = 55), and severe (n = 27 cases). The Mann-Whitney U test (MWT) was utilized for comparing the SICs of patients with different degrees of urticaria activity, and the results suggested great differences in levels of IL-17 and IL-31 among patients with mild, moderate, and severe urticaria activity. The specific values of relevant SICs were summarized in Table 3 below.
Table 3
SICs of patients with different degrees of urticaria activity
| SICs | Mild (n = 32) | Moderate (n = 55) | Severe (n = 27) | χ2 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTB4 [ng/ml] | 1.53 ±0.26 | 1.62 ±0.34 | 1.58 ±0.37 | 9.873 | 3.782 |
| LTC4 [ng/ml] | 2.41 ±0.52 | 2.56 ±0.32 | 2.51 ±0.56 | 10.256 | 2.607 |
| IL-4 [pg/ml] | 45.63 ±7.57 | 46.25 ±7.38 | 45.61 ±8.02 | 10.722 | 4.722 |
| IL-17 [pg/ml] | 3.42 ±0.46* | 3.98 ±0.78* | 4.42 ±1.03* | 22.562 | < 0.05 |
| IL-31 [pg/ml] | 17.35 ±8.25* | 30.15 ±8.76* | 41.46 ±10.81* | 23.134 | < 0.05 |
| TNF-γ [pg/ml] | 4.62 ±1.17 | 4.85 ±1.03 | 4.78 ±1.14 | 9.145 | 2.461 |
SICs of patients with different degrees of affected QOL
Table 4 listed the specific values of SICs of patients with different degrees of affected QOL. The IL-4 and IL-31 levels of patients positively associated with the CU-Q2oL score. Furthermore, according to the CU-Q2oL scores of patients, the QOL was slightly affected in 39 cases, moderately affected in 47 cases, and greatly affected in 28 cases. The MWT results revealed great differences in IL-4 and IL-31 levels among patients with different affected QOLs.
Table 4
SICs of patients with different affected QOLs
| SICs | Slightly affected QOL (n = 39) | Moderately affected QOL (n = 47) | Greatly affected QOL (n = 28) | χ2 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTB4 [ng/ml] | 1.36 ±0.52 | 1.54 ±0.63 | 1.4 ±0.35 | 11.683 | 5.257 |
| LTC4 [ng/ml] | 2.63 ±0.46 | 2.88 ±0.58 | 2.74 ±0.48 | 10.722 | 4.268 |
| IL-4 [pg/ml] | 40.67 ±8.03* | 44.36 ±7.81* | 47.02 ±7.35* | 20.562 | < 0.05 |
| IL-17 [pg/ml] | 3.48 ±0.51 | 3.87 ±0.55 | 3.62 ±0.72 | 9.577 | 4.062 |
| IL-31 [pg/ml] | 15.75 ±6.83* | 27.35 ±7.02* | 33.21 ±6.13* | 22.173 | < 0.05 |
| TNF-γ [pg/ml] | 4.45 ±1.03 | 4.81 ±1.16 | 4.62 ±0.89 | 12.637 | 4.145 |
Discussion
CSU is a prevalent dermatological condition characterized by symptoms such as skin itching, erythema, and oedema. Inflammation is a crucial pathophysiological mechanism of this disease, where immune cells release a cascade of inflammatory factors that affect skin cells and the nervous system, leading to itching and other symptoms. By analysing the levels of inflammatory factors in a patient’s serum, one can assess the immune status and degree of inflammatory response, which can reflect the severity of CSU and prognosis in patients. This is essential for devising treatment plans and monitoring treatment efficacy. In this study, 114 CSU patients were enrolled in the Res group, while 100 healthy individuals were enrolled in the Ctrl group. Levels of SICs were measured, including LTB4, LTC4, IL-4, IL-17, IL-31, and TNF-γ in both groups. The findings revealed significantly higher levels of LTB4, LTC4, IL-4, IL-17, and IL-31 in the Res group, while the TNF-γ level was greatly lower. In addition, correlations of each SIC to pruritus severity, duration of pruritus, urticaria activity, and QOL were examined.
The results revealed a statistically obvious difference (p < 0.05) in IL-4, IL-17, and IL-31 inflammatory factors among patients with mild, moderate, and severe pruritus. This difference in pruritus severity may indicate variations in immune status and inflammatory response levels, leading to differences in the levels of inflammatory factors. IL-4 and IL-17 are T cell-secreted inflammatory factors, while IL-31 is secreted by Th2 cells, dendritic cells, and mast cells. All of these factors are related to abnormal immune system activation and inflammatory response. Hence, the difference in the levels of these factors may indicate differences in immune system activation and inflammatory response in patients with CSU. However, the difference in the duration of pruritus among patients with different levels of inflammatory factors was not observable with p > 0.05. This could be due to the complex regulatory mechanisms that control the production and clearance of these factors, which are influenced by various factors such as metabolic status and physiological and pathological conditions. Thus, duration of pruritus may not be the most reliable indicator of disease progression and prognosis. Moreover, Góra et al. [17] found a correlation between multiple inflammatory factors and CSU, and these factors are associated with different immune cells and inflammatory mediators. Therefore, the interaction of various inflammatory factors may affect the severity and development of CSU.
Furthermore, this work revealed a positive association between the levels of IL-17 and IL-31 and urticaria activity in patients. The differences in serum IL-17 and IL-31 levels among patients with mild, moderate, and severe cases were greatly different, showing visible differences (p < 0.05). Additionally, the IL-4 and IL-31 levels were positively linked with the CU-Q2oL scores of patients, and the differences in serum IL-4 and IL-31 levels among patients with mild, moderate, and severe cases were great (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that SICs, including IL-17, IL-31, and IL-4, play a role in the pathogenesis of urticaria by regulating inflammatory responses, affecting cell proliferation, and mediating pathological immune reactions. Various factors such as genetics, environment, and lifestyle can influence the levels of these cytokines, affecting the incidence, development, and severity of the disease. For instance, Wang et al. [18] proved that elevated IL-4 can promote B cell proliferation and immunoglobulin E production, leading to increased sensitivity to allergens and exacerbation of the disease. Similarly Toubi and Vadasz [19] reported a positive correlation between disease severity and the level of IL-17 as IL-17 can promote the release of inflammatory mediators and chemokines by skin cells, increase inflammation and vascular permeability, and thus exacerbate the formation of wheals and itching symptoms [20, 21]. Additionally, IL-31 can enhance itching reactions and exacerbate itching symptoms in urticaria patients. Therefore, the levels of inflammatory cytokines are closely related to the pathogenesis, activity, and QOL of CSU and have significant reference value in studying the mechanisms, evaluating the severity of the disease, and guiding treatment.
Conclusions
The experimental findings of this work demonstrated a positive association between serum levels of IL-4, IL-17, and IL-31 in CSU patients and the severity of CSU as well as the QOL scores. Although the precise roles of these SICs in different clinical presentations required further investigation, these results suggested their potential as biomarkers for evaluating CSU severity. Therefore, it was recommended to further explore the underlying mechanisms of these SICs in clinical practice to yield more evidence-based guidance for CSU treatment. However, this work was subject to several limitations, such as a relatively small sample size and potential sample selection bias. Additionally, it only investigated a limited number of SICs, and other potential cytokines related to urticaria were not included and analysed. To this end, future studies could be made by expanding the sample size to investigate more SICs and to establish a more comprehensive and systematic model. At the same time, the clinical data and living habits of patients were analysed to improve the reliability and universality of the study. Therefore, analysing the serum levels of SICs provided crucial insight into the immune status and degree of inflammation of patients, which is essential for understanding the pathogenesis and prognosis of urticaria.