Summary
Ablation index–guided high-power radiofrequency ablation combined with impedance spike cut-off appears to be a safe and effective ablation technique for atrial fibrillation.
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia in elderly individuals, which constitutes a significant public health problem [1]. With ageing populations, AF was predicted to affect 6–12 million people in the USA by 2050 and 17.9 million in Europe by 2060 [2, 3]. The incidence of AF is progressively increasing due to aging of the population [3]. AF is associated with increased morbidity, especially stroke and heart failure, as well as increased mortality [1]. Approximately 80–95% of AF cases are caused by focal electrical discharges emerging from the pulmonary veins [4]. Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is the cornerstone of current AF radiofrequency ablation (RFA) techniques, with the greatest efficacy in patients with atrial fibrillation [5].
High-power RFA has emerged as a novel approach for AF to improve procedure effectiveness. Previously published studies have shown that the utility of high-power, short-duration (50–80 W for 5 s) ablation could achieve similar lesion depth with fewer complications compared to conventional lower-power and longer-duration settings (20–30 W for 30 s) [6, 7]. Also, very high-power, short-duration (90-W/4-second) ablation for pulmonary PVI has been considered an acute effective, safe surgical method that could also reduce procedural times [8–10]. With the gradual increase in ablation energy, the immediate success rate of AF did not seem to decrease while shortening the operation time, but the long-term success rate under the high-power, short-duration strategy still needs further clarification.
The ablation index is a marker incorporating contact force, time, and power in a weighted formula. The latest meta-analysis revealed that the ablation index–guided procedure resulted in a significantly shorter fluoroscopy time and total ablation time, higher first-pass isolation, and lower acute pulmonary vein reconnection [8]. Another meta-analysis also suggested that ablation index–guided catheter ablation is associated with increased efficacy of AF ablation, while preserving a comparable safety profile [9]. Impedance spike cut-off is an auxiliary function in some integrated radiofrequency (RF) generator systems, such as the SMARTABLATE generator (Biosense Webster, Irvine, CA, USA). If the impedance spikes higher than the number set here in any half second interval, the RF energy will automatically shut off to avoid steam pops. To our best knowledge, there is no published research to evaluate its impact on safety during catheter ablation, including when used with the ablation index.
Aim
The primary objective of the study is to evaluate the procedural efficiency, safety, and effectiveness outcomes associated with the use of ablation index–guided high-power (AI HP) RFA by impedance spike cut-off for AF during 1- and 3-year follow-up.
Material and methods
Study design
This single-center, retrospective real-world study used the de-identified data retrieved from the electronic medical records (EMR) at the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China, from June 2019 to June 2020. The study was approved by the hospital (KY 2019080). The inclusion criteria were: (1) age > 18 years old; (2) underwent primary radiofrequency catheter ablation. Patients were excluded if they met any of the following criteria: (1) left atrial (LA) diameter > 50 mm, (2) uncontrolled heart failure or NYHA function class III or IV, (3) life expectancy less than 12 months.
Ablation procedure and follow-up
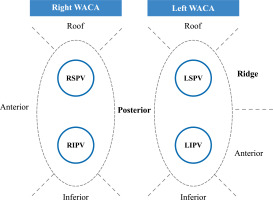
All procedures were performed under general anesthesia. Fast anatomical mapping of the left atrium was performed with the PentaRay catheter. Subsequently, all patients underwent bilateral PVI. Ablation index–guided point-by-point ablation encircling ipsilateral pulmonary veins was performed using a Thermocool SmartTouch SF (STSF) catheter. Ablation power was set to 40–50 W, targeting ablation index values (480–500 anterior, 400–420 inferior and posterior, 460–480 roof and 500–520 ridge) and interlesion distance ≤ 6 mm (Figure 1). The spike cut-off on the generator was set to 15% of the baseline drop within 1 s. If the impedance spikes higher than the number set, the RFA energy will be automatically shut off by the RFA generator within 1 s. The Visitag Module was used to visualize RFA applications using the following stability criteria: 2.5 mm maximum range, 3 s. minimum time, 2 maximum point size. The patients who underwent BOX ablation in addition to PVI were those with low-voltage areas in the posterior wall of the atrium, specifically areas where the bipolar voltage in the posterior wall is less than 0.5 mV. Following this, a 20-minute waiting period was observed to uncover any dormant conduction.
Figure 1
Nine segments in the radiofrequency ablation procedures
WACA – wide area circumferential ablation, RIPV – right inferior pulmonary vein, RSPV – right superior pulmonary vein, LIPV – left inferior pulmonary vein, LSPV – left superior pulmonary vein.
Outpatient clinical visits were planned at 3, 6, 9, 12 months, and 3 years after the procedure. During the first year of follow-up, patients received a 7-day Holter at each visit. For follow-up between 1 and 3 years, the assessment method was a 24-hour Holter. AF recurrence was defined as episodes of any atrial arrhythmias lasting ≥ 30 s.
Study outcomes
The following main procedural endpoints were included in the evaluation of outcomes: acute PVI success rate, procedure time, total RFA time, fluoroscopy time and dose, first-pass PVI rate, impedance value, the number of pulmonary vein application, spike cut-off rate and segments. Ablation lesions’ ablation index value per lesion, RF time per lesion, impedance drop per lesion, and contact force per lesion were also evaluated.
The long-term effectiveness endpoint was examined by AF recurrence rate during 1- and 3-year follow-up. The safety endpoints included the incidence of acute (within 7 days of procedure) and chronic procedure/device related complications up to 1 year.
Statistical analysis
Patients were excluded from the analysis without imputation if they were lost to follow-up or died prior to the last follow-up. Descriptive statistics and statistical comparison were used to evaluate the baseline, effectiveness, efficiency, and safety endpoints. Descriptive analyses were reported as mean (standard deviation) for continuous variables, or count and percentage for categorical variables. The time to recurrence was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
In addition, a subgroup analysis was also conducted in this study. The included patients were divided into two subgroups according to whether the patient was diagnosed with persistent AF (PsAF) or paroxysmal AF (PAF). PAF was defined as AF that is intermittent and terminates within 7 days of onset; PsAF was defined as AF that is continuous and sustained for > 7 days and requires intervention. Baseline characteristics and all study outcomes were compared between the two subgroups. The study applied Welch’s t-test when appropriate for continuous variables and the χ2 test for categorical variables to determine whether the differences observed across the two subgroups were significant.
The Cox proportional-hazards model was used to analyze the correlation between baseline and intraoperative characteristics and recurrence during 1-year follow-up. R (version 4.0.1) software was used to perform the statistical analyses in this study. All statistical comparisons were two-sided tests at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics
A total of 150 patients underwent high-power RFA. According to the exclusion criteria, 18 patients were excluded (Figure 2), resulting in the final inclusion of 132 patients. Among the excluded patients, there were 2 deaths; one occurred 8 months after surgery due to acute myocardial infarction, and the other was reported as an accidental death by family members during the 6-month follow-up. Table I summarizes patients’ baseline demographic and clinical characteristics. The heart rate (HR) was measured during sinus rhythm. At the same time, although there was a statistically significant difference in left ventricular ejection (LVEF) fraction between the two groups, both were normal (> 60%), thus lacking clinical significance.
Figure 2
Patient flowchart. The flowchart shows the number of patients included in the study following the inclusion and exclusion criteria mentioned in the Material and methods
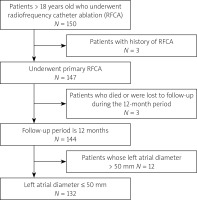
Table I
Baseline characteristics
Procedural efficiency
Procedural efficiency is presented in Tables II and III. Table II mainly summarizes the results of intraoperative related parameters, including operation time, fluoroscopy dose, PVI success rate, etc. Table III mainly presents the patients who experienced impedance spike cut-off and their relative locations.
Table II
Procedural efficiency
Table III
Impedance spike cut-off summary
Lesion analysis
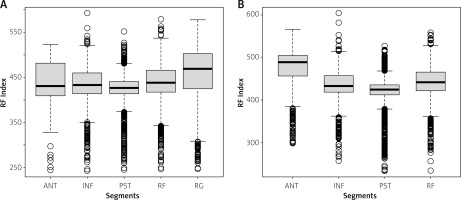
As 2 patients’ lesion records were lost for technical reasons, the lesion data of 130 patients were collected and analyzed. The analysis of relevant parameters is shown in Table IV and Figure 3.
Table IV
Lesion analysis
Long-term effectiveness
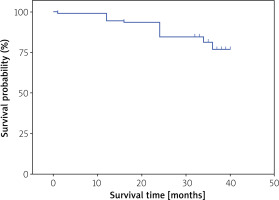
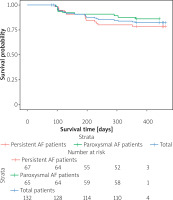
The Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that at 1- and 3-year follow-up, the 1-year postoperative freedom from any documented atrial arrhythmias lasting more than 30 s on ECG was 82.6% (109/132), and the 3-year freedom was 77.06% (84/109) (Figures 4 and 5). The results in PAF and PsAF subgroups were similar (86.2% vs. 79.1%, p = 0.402). Among those patients with recurrence, six underwent repeat ablation. Cox regression analysis showed that female sex, procedure time, baseline impedance value, and contact force were independent prognostic factors for recurrence during 12-month follow-up (Table V).
Figure 4
Survival rate for atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence-free survival within 1-year after catheter ablation in total group, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) patients, and persistent atrial fibrillation (PsAF) patients
Safety analysis
Among the 132 patients enrolled, only two audible steam pops without clinical sequelae occurred, which might be due to a sudden increase in contact force (40–45 g) that happened at the anterior of LIPV and the anterior of RPV, respectively. One of the 2 patients had pericardial tamponade during the procedure. The patient had an audible steam pop following pericardial effusion when the STSF was located at the anterior of the LIPV. No spike cut-off occurred when the maximum contact force was 45 g. No other procedure/device-related complications occurred.
Discussion
The key findings of this study were: (1) the AI HP and short duration approach combined with impedance spike cut-off for the treatment of AF demonstrates high safety and efficacy during the 1-year and 3-year follow-up; (2) impedance spike cut-off events most frequently occurred at the anterior carina and inferior portion of the RPV, the ridge between the left atrial appendage, and the left pulmonary vein.
The quality of the ablation lesion is essential to prevent pulmonary vein reconnection, which is a major determining factor of AF recurrence [11–15]. The physical properties of the lesion during RFA are related to the ablation power, contact force, ablation duration, catheter stability, and the electrode diameter of the catheter [16]. Compared with conventional RFA using moderate power (20–40 W) for a relatively long duration (20–40 s) at a contact force (CF) of 10–20 g, higher power combined with shortened application time may improve catheter stability in a beating heart and lead to more effective lesion formation, characterized by adequate depth and continuity [17]. Recently, a series of experimental and observational studies assessing the effectiveness and safety of high-power ablation has been conducted. One study employing unregulated high-power ablation (50 W) for PVI demonstrated a significantly shorter fluoroscopic time and procedure time; however, this was accompanied by an increased risk of complications [18]. Another randomized controlled trial comparing high power with moderate power ablation showed a shorter ablation time with a similar complication rate and a similar 12-month recurrence rate [17]. Our study found that the overall freedom from any atrial arrhythmias was 82.6% during the 1-year follow-up and 77.1% during the 3-year follow-up. This result was similar to that reported in other high-power, short duration studies [19–22]. However, the higher success rate shown by the 3-year follow-up results may also have an expanding component. On one hand, it may be related to our 1-year prognostic detection method being 24-hour Holter monitoring, which might overlook the occurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation; on the other hand, the patients with PAF in our study accounted for 49.2%, and PAF has a better prognosis compared to persistent atrial fibrillation, which may also affect the results. Female sex, procedure time, baseline impedance value, and CF were independent prognostic factors for AF recurrence.
In our study, high-power ablation achieved a 100% acute procedural success rate, and first-pass PVI was 87.9%, which indicates creation of a high-quality, contiguous lesion. Regarding efficiency, our study’s relatively short total procedure time (55 min), ablation time (36 min), and fluoroscopy time (7 min) reflected a faster PVI procedure compared to traditional power ablation procedures, consistent with other high-power ablation studies, even though 49.2% of our patients had PsAF [23–25].
Previous studies have found that with the increase of radiofrequency energy, the risk of steam pop occurring during the procedure also increases [26]. Furthermore, research has shown a good correlation between the increase in radiofrequency energy and the decrease in impedance [27]. In a prospective observational study, the relationship between various catheter parameters and the occurrence rate of audible steam pops during left atrial ablation was investigated, with 59 (26.1%) cases of audible steam pops reported in 226 patients [21]. Therefore, by setting a specific threshold for impedance decrease, the system will automatically stop the release of energy once the relevant threshold is reached, which theoretically can reduce the occurrence of steam pop during the procedure and increase the safety of the surgery. Also, our findings prove that employing impedance spike cut-off during RFA can effectively prevent steam-pops and consequently reduce procedural complications, such as cardiac tamponade, as evidenced by the low incidence of cardiac tamponade observed in our study (0.8%). This conclusion is also supported by our prior research, which demonstrated that impedance cutoff significantly reduces the incidence of intraoperative steam pops and cardiac tamponade [28].
At the same time, we also analyzed the locations where impedance spike cutoff is likely to occur. We found that impedance spike cut-off events most frequently occurred at the anterior carina and inferior portion of the RPV and the ridge between the left atrial appendage and the left pulmonary vein. This indicates that these areas may be prone to steam pop, so by identifying the areas where impedance rapidly decreases, along with impedance spike cut-off, it may increase intraoperative safety and reduce the occurrence of related complications.
To our knowledge, there have been few reports on the application of impedance cut-off. In this study, we set up an impedance spike cut-off procedure, but 2 patients still experienced steam pop. Our analysis found that the impedance of these 2 patients did not reach the set threshold, which may be due to a sudden increase in CF. Therefore, the occurrence of steam pop is a result of multiple factors. Rapid impedance drop helps us identify and prevent the occurrence of steam pop, but attention still needs to be paid to key parameters such as pressure.
In evaluating the complications of high-power ablation, silent cerebral embolism is a significant aspect that cannot be overlooked. Previous studies have shown inconsistent results regarding the incidence of silent cerebral embolism after high-power ablation, with some results indicating a higher incidence of 24–26% [29], while others show no difference compared to standard ablation [30, 31]. However, in our study, due to the lack of comprehensive cranial imaging examinations in patients, we were unable to make corresponding assessments regarding the occurrence of silent cerebral embolism.
Limitations. First, it is a retrospective, single-arm, single-center study, and during the follow-up process, some patients were released, which may have led to bias in the results. Future multicenter cohort studies should be conducted to strengthen the evidence supporting the research findings. Second, the locations of impedance spike cut-off and gaps were not recorded according to the nine segments in the lesion analysis, making it hard to analyze the correlation between the ablation parameters and the events. However, the exploration of the location of the impedance spike cut-off is indeed an interesting result that may help operators identify where steam eruptions are likely to occur.