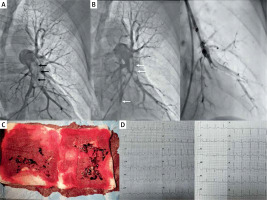
A 59-year-old man with a history of colon cancer treated surgically three weeks ago was admitted with sudden dyspnoea and chest pain. Three days earlier he developed deep vein thrombosis of the left lower extremity and was treated with full dose low-molecular weight heparin. Physical examination revealed blood pressure 125/70 mm Hg, heart rate 125/min, respiratory rate 28/min. In laboratory tests NT-proBNP was 1961 pg/ml, troponin I 0.4 mg/dl (r.v. < 0.01 mg/dl), arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) 88%. Echocardiography revealed signs of right ventricular (RV) enlargement (RV/LV index = 1.9) and hypokinesis of the free RV wall. In computed tomography bilateral massive thrombi affecting lobar pulmonary arteries were observed. Based on these results the patient was diagnosed with intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism (PE). Calculated PESI score was 139 points (class V – very high risk). Due to relative contraindications to systemic thrombolysis our local Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT) decided to treat this patient with catheter-directed thrombectomy (CDT). Pulmonary angiography was made from right femoral vein access and revealed massive PE especially in the left pulmonary artery (Figure 1 A) [1]. Pulmonary artery pressure was 45/22/32 mm Hg. An intravenous bolus of 7000 IU of unfractionated heparin was administered at the beginning of the procedure. Continuous mechanical aspiration thrombectomy was subsequently performed with a 115 cm 8 Fr Indigo CAT8 TORQ catheter (Penumbra, Almeda, Ca, USA). A separator wire was repeatedly passed through the thrombus to break it down and allow it to be suctioned through the catheter. The thrombus was fragmented and partially removed (Figure 1 B) but distal embolization in the intermediate branch and lower segmental branches appeared (A4-5, A10). For this reason we continued aspiration and entered selectively segmental branches using the support of 6 Fr Judkins Right diagnostic coronary catheter and 0.014′′ coronary guide-wire to restore and improve the pulmonary flow (Figure 1 B). The decision to terminate the procedure was taken after evaluation of haemodynamic parameters (pulmonary artery pressure decreased to 28/11/16 mm Hg and SaO2 to 93%) and also the total amount of aspirated blood (350 ml). After the procedure the clinical status of the patient rapidly improved. Anticoagulation was continued with body weight-adjusted low-molecular-weight heparin. On the second day after the procedure normalisation of ECG (Figure 1 D) and echocardiography were obtained and SaO2 increased to 96% (without oxygen supplementation). On discharge (day 4) NT-proBNP levels dropped to 162 pg/ml and troponin I to 0.013 ng/ml. The patient was discharged home in good clinical condition on full-dose enoxaparin s.c. due to neoplastic disease.
Figure 1
A – Angiogram of the left pulmonary artery before the procedure. Right anterior oblique 30° projection was used to determine the segmental arteries accurately [1]. The massive thrombus affecting lower lobar arteries is visible. B – Angiogram after continuous aspiration thrombectomy with Indigo 8 Fr catheter. The thrombus was fragmented and mostly removed, but distal embolization of segmental branches of the intermediate lobe and lower lobe (white arrows) prompted us to continue aspiration. 6 Fr Judkins Right coronary catheter and coronary guidewire were used to selectively intubate segmental arteries and to restore the flow. C – Aspirated thrombi from the pulmonary artery. D – ECG before the procedure. Sinus rhythm of 115/min with right bundle branch block and signs of right ventricular overload. ECG on next day after the procedure revealed sinus rhythm of 88/min. RBBB completely subsided
Interestingly, the improvement in clinical, haemodynamic and respiratory status was rapidly obtained without achieving complete thrombus removal. Even partial improvement of pulmonary flow can restore sufficient cardiac output and reverse heart overload [2]. Distal embolization during mechanical thrombectomy might however limit the flow to the segmental branches and increase pulmonary arterial resistance even despite continuous aspiration. One should take care of the axial position of the catheter and continue the procedure in distal arteries until the flow is restored. The role of CDT in intermediate-high risk PE patients is still not well established and randomised trials remain rare [3]. However, fast development of the technique and new devices made aspiration CDT easy and safely applicable. It may lead to fast improvement of haemodynamic and clinical status and seems to be a reasonable alternative for intermediate-high risk PE especially in patients with contraindications to systemic thrombolysis or high bleeding risk [3, 4].







