Summary
The research demonstrated that among non-diabetic patients, the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) was significantly associated with 5-year all-cause mortality in acute decompensated chronic heart failure (ADCHF) patients but not in de novo heart failure (DNHF) patients. Differentiating the predictive value of TyG between DNHF and ADCHF patients could enhance our understanding and refine treatment strategies for individuals with acute heart failure.
Introduction
Recent studies have increasingly emphasized the significant associations between heart failure (HF) and insulin resistance (IR). Prior research has confirmed diminished insulin sensitivity and responsiveness in individuals with HF but without diabetes mellitus (DM) [1, 2]. Moreover, the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) has been widely adopted in clinical practice as a simple and reliable biomarker for diagnosing peripheral IR [3, 4]. Extensive studies have demonstrated that TyG outperforms the homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA) in evaluating IR [5, 6]. In addition, TyG has been shown to have a strong predictive value for AHF patients without diabetes [7].
De novo heart failure (DNHF) and acute decompensated chronic heart failure (ADCHF) represent two distinct subtypes of acute heart failure (AHF). These subgroups exhibit marked heterogeneity within the same syndrome [8]. Compared with DNHF patients, ADCHF patients typically present with a worse baseline health status and a higher prevalence of comorbidities, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and atrial fibrillation (AF). Laboratory findings in ADCHF patients, including lower albumin levels, tend to be more unfavorable than those in DNHF patients, reflecting greater admission severity [9]. Additionally, ADCHF patients demonstrate poorer short- and long-term outcomes compared to DNHF patients. Furthermore, ADCHF predominantly occurs in the middle and late stages of heart failure, with a longer duration of heart failure compared to DNHF [10, 11]. Stronger activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and sympatho-adrenergic system, more severe systemic metabolic disturbances, elevated expression of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, and increased cellular oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress contribute to significant inhibition of the insulin signaling pathway in ADCHF patients [12–15]. This ultimately results in more pronounced IR. Consequently, the two AHF subtypes may exhibit distinct TyG levels, with the prognostic significance of TyG varying according to the AHF subtype.
Aim
This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of the TyG index among non-diabetic individuals with ADCHF and DNHF.
Material and methods
Patients
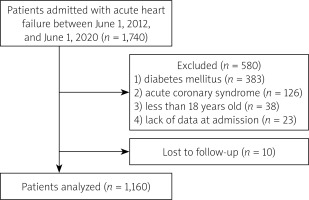
This retrospective analysis examined data collected from 1,740 consecutive patients with AHF admitted to our hospital between June 1, 2012, and June 1, 2020. The diagnoses of acute and chronic heart failure were established in accordance with the 2021 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines [16]. A total of 580 patients were excluded based on the following criteria: 1) presence of diabetes mellitus (DM); 2) acute coronary syndrome (ACS); 3) age below 18 years; 4) loss of monitoring data; and 5) insufficient medical information upon admission. Consequently, the final study population consisted of 1160 patients (Figure 1).
Data collection and diagnostic criteria
Patient demographics, clinical history, laboratory test results, and echocardiographic measurements were collected from the electronic health information database. Additionally, we documented the medication regimens of patients at admission, including vasoactive medications (e.g., phentolamine, nitroglycerin, dopamine), renin-angiotensin system inhibitors (RASIs), β-blockers, and statins. After an overnight fasting period exceeding 8 h, the first set of peripheral venous blood samples was drawn and analyzed in the laboratory. For patients with suspected diabetes, we routinely performed the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). Diabetes was diagnosed based on OGTT results or a self-reported medical history of the condition. Hypertension was defined as a systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mm Hg and/or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mm Hg, the use of antihypertensive medications, or a documented family history of hypertension.
Two distinct patient profiles were identified in AHF cases: 1) DNHF, referred to as new-onset HF, includes patients with no prior history or documented evidence of HF in their health records; 2) ADCHF is defined as the worsening of previously diagnosed HF, as indicated by clinical signs or documented in health records.
Measurements
Measurements were conducted for blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum sodium (Na), total cholesterol (TC), hemoglobin (Hb), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), C-reactive protein (CRP), serum albumin, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP).
Using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) levels were calculated [17]. The mortality risk score was determined using the Enhanced Feedback for Effective Cardiac Treatment (EFFECT) methodology [18]. This risk prediction model is specifically designed for use in hospitalized patients presenting with heart failure (HF), enabling risk stratification within a few hours of admission. The scores were categorized into five groups: very low risk (< 60), low risk (61–90), moderate risk (91–120), high risk (121–150), and very high risk (> 150) [14]. TyG calculation: TyG = ln [fasting triglyceride (mg/dl) × fasting plasma glucose (mg/dl)/2].
Follow-up
Patients were followed for 5 years. The study’s primary endpoint was all-cause mortality. Skilled nurses conducted follow-up calls or visits with patients in the clinic every 6 months to monitor their conditions.
Statistical analysis
Sample size calculation: the expected sensitivity and specificity of TyG in predicting the prognosis of HF patients were 80% and 60%, respectively. When the allowable error was 8% (Δ) and the two-sided α level of statistical significance was 0.05, the sample size for the ADCHF group was calculated according to the sensitivity and the sample size for the DNHF group was calculated according to the specificity. There were 97 cases in the ADCHF group and 145 cases in the DNHF group. The calculation formula is as follows:
The median [interquartile range (IQR)] and mean ± standard deviation (SD) were used to report continuous variables with skewed and normal distributions, respectively. Categorical variables were expressed numerically (%). Categorical variables were compared between groups using the χ2 test. Depending on the circumstances, the paired Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous data. All comparisons were carried out using two-tailed tests. The association between patient group categories and all-cause mortality was assessed using Cox proportional hazards regression analyses, both unadjusted and adjusted. Variables with p < 0.10 in the univariate analysis were analyzed using multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression. The survival analysis was performed with the R program using Kaplan-Meier methods. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under the curve (AUC) were constructed to assess the predictive capability of the TyG index for 5-year all-cause mortality in both ADCHF and DNHF patients. Furthermore, restricted cubic spline analysis was performed to illustrate the dose-response relationship between TyG and the risk of 5-year mortality in these patient populations. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 (for the Bonferroni correction, this was based on adjusted p-values). The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25.0 (IBM, Armonk, New York, United States), R studio, and R version 4.2.1.
Results
General characteristics of patients
Of the 1740 potential AHF patients, 1160 were selected for analysis. According to the predefined classification criteria, 624 (53.8%) patients were categorized as having ADCHF, while 536 (46.2%) were classified as having DNHF. Notably, DNHF patients exhibited significantly lower TyG index levels compared to ADCHF patients (median 8.72 vs. 10.36, p < 0.001), with an overall median TyG index of 9.36. Table I summarizes the baseline characteristics stratified by AHF subtype. ADCHF patients were generally older and demonstrated a higher EFFECT mortality risk score compared to DNHF patients. Furthermore, a significantly greater proportion of ADCHF patients required nitroglycerin therapy (all p < 0.001). Additionally, ADCHF patients were more likely to experience cardiogenic shock and require norepinephrine support (p < 0.05). Consistently, ADCHF patients had longer hospital stays and exhibited higher 5-year all-cause mortality rates compared to DNHF patients (all p < 0.05).
ADCHF patients exhibited significantly higher proportions of individuals with abnormal levels of glucose, serum albumin, TC, TG, and LDL-C, as well as a greater prevalence of comorbidities, including hypertension (HTN), coronary heart disease (CHD), cerebrovascular accident (CVA), atrial fibrillation (AF), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (all p < 0.05). Based on echocardiographic assessments, ADCHF patients demonstrated larger left atrium and left ventricle diameters compared to DNHF patients (all p < 0.001) (Table I).
Table I
Baseline characteristics according to heart failure type. Comparison of categorical variables conducted using the χ2 test. Comparison of continuous variables conducted using the paired Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney test. Values are means (standard deviations), n (%, percentages), or medians (interquartile ranges)
[i] DNHF – de novo heart failure, ADCHF – acute decompensated chronic heart failure, EFFECT score – Enhanced Feedback for Effective Cardiac Treatment mortality risk score, SBP – systolic blood pressure, DBP – diastolic blood pressure, HR – heart rate, eGFR – estimated glomerular filtration rate, NT-proBNP – N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide, CRP – C-reactive protein, TC – total cholesterol, TG – triglyceride, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein, BUN – blood urea nitrogen, Na – sodium, Hb – hemoglobin, TyG – triglyceride-glucose index, HbA1c – hemoglobin A1c, HTN – hypertension, CHD – coronary heart disease, AF – atrial fibrillation, CVA – cerebrovascular accident, COPD – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, LVDD – left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, LAD – left atrial diameter, LVEF – left ventricular ejection fraction, RASI – renin–angiotensin-system inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker), LOS – length of stay.
Relationship between TyG and 5-year all-cause mortality differed between patients with DNHF and those with ADCHF
DNHF patients demonstrated a significantly lower incidence of all-cause mortality compared to ADCHF patients over a 5-year period (log-rank p < 0.001; Figure 2 A). Figures 2 B and C illustrate the Kaplan-Meier survival curves for 5-year all-cause mortality in DNHF and ADCHF patients, stratified by median TyG levels. ADCHF patients with lower TyG levels exhibited fewer mortality events compared to those with higher TyG levels (log-rank p < 0.001). In contrast, DNHF patients in both low- and high-TyG groups did not exhibit significant differences in 5-year all-cause mortality (Log-rank p = 0.97). A Cox proportional hazards regression analysis revealed that TyG was an independent predictor of 5-year all-cause mortality in ADCHF patients (univariate unadjusted HR = 7.68 [95% CI: 4.67–12.65], p < 0.001; multivariable adjusted HR = 2.72 [95% CI: 1.93–3.85], p < 0.001). Conversely, TyG was not associated with all-cause mortality in DNHF patients (univariate unadjusted HR = 1.15 [95% CI: 0.68–1.94], p = 0.61) (Table II).
Figure 2
Kaplan-Meier analysis of all-cause mortality in various types of acute heart failure. A – the 5-year all-cause mortality stratified by the type of acute heart failure. B, C – the 5-year allcause mortality in patients with DNHF and ADCHF, respectively, categorized by the median TyG
DNHF – de novo heart failure, ADCHF – acute decompensated chronic heart failure, DNH – de novo heart failure patients with higher TyG levels than the median level, DNL – de novo heart failure patients with lower TyG levels than the median level, ADH – acute decompensated chronic heart failure patients with higher TyG levels than the median level, ADL – acute decompensated chronic heart failure patients with lower TyG levels than the median level. TyG – triglyceride-glucose index.
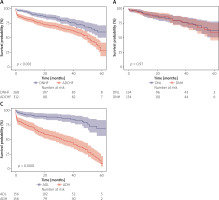
Table II
Prognostic significance of the triglyceride-glucose index in patients with de novo heart failure and acute decompensated chronic heart failure. Categories: DNHF – all 536 cases of DNHF were included in the Cox proportional hazards analysis; ADCHF – all 624 cases of ADCHF were included in the Cox proportional hazards analysis. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was performed, adjusting for age, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular accident, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, systolic blood pressure, B-type natriuretic peptide, C-reactive protein, albumin, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, serum sodium, hemoglobin A1c, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, left atrial diameter, left ventricular ejection fraction, use of nitroglycerin, norepinephrine, and the EFFECT mortality risk score
| Parameter | Univariate | P-value | Multivariate | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |||
| DNHF | ||||
| TyG | 1.15 (0.68-1.94) | 0.612 | NA | NA |
| ADCHF | ||||
| TyG | 7.68 (4.67–12.65) | < 0.001 | 2.72 (1.93–3.85) | < 0.001 |
Difference in prognostic predictive value of TyG between DNHF patients and ADCHF patients
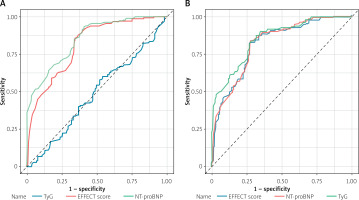
ROC curve analysis was used to assess the clinical value of TyG in predicting 5-year all-cause mortality in DNHF and ADCHF patients. In DNHF patients, TyG has no predictive value for 5-year mortality. In patients with ADCHF, TyG had a good predictive power for 5-year mortality and was superior to the EFFECT mortality risk score and NT-proBNP (Figure 3).
Figure 3
The ROC curve was used to assess the predictive value of TyG for 5-year all-cause mortality in patients with DNHF and ADCHF. A – In DNHF patients, the AUC values for TyG, NT-proBNP, and EFFECT score were 0.488 (95% CI: 0.436–0.539), 0.852 (95% CI: 0.436–0.539), and 0.819 (95% CI: 0.789–0.884), respectively. B – In ADCHF patients, the AUC values for TyG, NT-proBNP, and EFFECT score were 0.852 (95% CI: 0.821–0.884), 0.822 (95% CI: 0.789–0.855), and 0.814 (95% CI: 0.779–0.849), respectively
ROC curve – receiver operating characteristic curve, DNHF – de novo heart failure, ADCHF – acute decompensated chronic heart failure, TyG – triglyceride-glucose index, EFFECT mortality risk score – enhanced Feedback for Effective Cardiac Treatment mortality risk score, NT-proBNP – N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide, AUC – area under the curve.
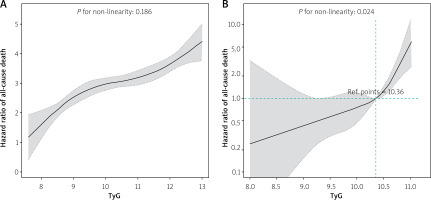
The dose-response relationship between TyG and 5-year all-cause mortality risk was assessed using restricted cubic spline analysis. The findings indicated that TyG was not significantly associated with 5-year all-cause mortality risk in DNHF patients (nonlinear p = 0.19). In contrast, among ADCHF patients, the risk of all-cause mortality in non-diabetic AHF patients was significantly elevated when TyG values exceeded 10.36 (hazard ratio increased by 2.96 per standard deviation increase in TyG, 95% CI: 2.48–3.52, nonlinear p = 0.024) (Figure 4).
Figure 4
Unadjusted (A) and multivariable-adjusted (B) hazard ratios for 5-year all-cause mortality based on restricted cubic splines of the TyG index. A – specifically addresses DNHF patients, while B – focuses on ADCHF patients. The black line represents the reference hazard ratio, and the gray shaded area denotes the 95% confidence intervals. The multivariable-adjusted model for ADCHF was further adjusted for the following covariates: gender, age, estimated glomerular filtration rate, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, serum albumin, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, left atrial diameter, left ventricular ejection fraction, cardiogenic shock, coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular accident, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, any valvular heart disease, and the use of vasoactive drugs
DNHF – de novo heart failure, ADCHF – acute decompensated chronic heart failure, TyG – triglyceride-glucose index.
Discussion
In this retrospective study, we identified a novel association between the TyG index and the risk of all-cause mortality in ADCHF patients without diabetes mellitus for the first time. Our findings demonstrate that TyG serves as an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in these patients. Interestingly, no significant effect of TyG on prognosis was observed in DNHF patients. Moreover, ADCHF patients with TyG levels above the median exhibited worse 5-year all-cause mortality outcomes compared to those below the median. These results indicate that TyG has robust predictive power for 5-year all-cause mortality in ADCHF patients, whereas no comparable association was found in DNHF patients.
Previous studies have confirmed reduced sensitivity and responsiveness to insulin in patients with HF without DM [1]. Therefore, in non-diabetic ADCHF patients, IR also induces an imbalance in endothelial dysfunction, glucolipid metabolism and triggers oxidative stress, inflammation, and ectopic lipid accumulation, among other processes, which are related to prognostic risk in HF patients [19–22]. IR is both an etiology and a consequence of HF, and it is a pathophysiological feature of HF that affects symptoms, mortality, and prognosis [23–25]. This suggests that TyG, a reliable marker of IR, could be a potent predictor of adverse events in HF patients even without diabetes.
A more severe IR was represented by an elevated level of TyG [26]. An increase in serum cytokine production may help to explain the connection between IR severity and sickness. These products have been demonstrated to rise with illness severity and to be important components of the inflammatory process and stress-induced IR [27, 28]. In addition, even in those who had never had diabetes before, critically sick patients frequently experienced hyperglycemia related to IR [29]. Hyperglycemia is commonly caused by stress-induced IR, which is mediated by antagonistic hormones (epinephrine, the neurotransmitter glucagon, adrenaline, maturation hormone) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6) [30]. In contrast, more severe tissue structural failure resulted from hyperglycemia’s promotion of tissue acidosis, formation of reactive oxygen compounds and nitrogen, and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Therefore, an elevated level of TyG was associated with more critical condition and short-term and long-term adverse events [26, 31]. This could explain why the medical results for 5-year all-cause death were worse in ADCHF patients with TyG levels higher than the current study’s median.
However, in an experimental animal study, Fu et al. found that insulin sensitivity did not change in the early stage of new-onset HF. Instead, it appeared with the progression of HF and gradually increased with the duration of the disease. This suggests that IR is present in patients with ADCHF but rare in patients with DNHF, and IR is one of the manifestations of heterogeneity between DNHF and ADCHF. Therefore, TyG was substantially lower in the DNHF patients than in the ADCHF patients, and the prognostic value of TyG was different in both types of heart failure.
Similar to previous studies, we observed that all-cause death in patients with ADCHF was considerably higher than in DNHF patients, both in the short term (hospitalization and 30 days) and in the long term (1 year and 5 years) [10, 32–34]. In addition, the two patient groups show significant differences in survival rate over time. ADCHF patients are primarily characterized by symptoms and signs of congestion and fluid retention, which are hallmarks of acute left ventricular systolic failure. This explains the significantly greater use of intravenous nitroglycerin in ADCHF patients than in DNHF patients in our study. The above clinical features of ADCHF patients are due to the protracted, frequently dysregulated neuro-humoral compensatory mechanisms that work to preserve the circulatory status quo in spite of deteriorating left ventricular performance. When the balance leans toward fluid overload and the compensatory mechanisms fall short or perhaps fail entirely, decompensation takes place [35]. This appears to underline that DNHF and ADCHF are distinct conditions. In fact, previous studies have found that cardiac dysfunction in some types of DNHF is temporary in nature and may therefore be curable along with the precipitating conditions such as coronary heart disease [36]. This suggests the importance of curing the underlying etiology of DNHF to prevent DNHF from progressing to ADCHF. This could at least partially explain why DNHF patients have a better prognosis at both short- and long-term follow-up.
We found that ADCHF patients were older and had more comorbidities such as HTN, CHD, CVA, AF, and COPD compared to those with DNHF. In addition, ADCHF patients had a lower albumin level and higher EFFECT mortality risk score. Furthermore, more ADCHF patients suffered from cardiogenic shock and required norepinephrine. This suggests that ADCHF patients exhibited worse severity of conditions on admission compared with the DNHF patients. Moreover, glucose, TC, TG, and LDL levels were higher in the ADCHF patients. In terms of echocardiographic findings, ADCHF patients had greater left atrial and left ventricle sizes than those with DNHF. Similar results were obtained in previous studies, suggesting that DNHF and ADCHF have different characteristics and pathophysiological states [11, 21, 37, 38]. As a result, these discrepancies may cause a variety of poor consequences in individuals with DNHF and
ADCHF in addition to altering TyG levels. Nevertheless, after correcting all clinical variables, TyG was found to be an essential predictive marker for ADCHF but not in DNHF. This suggests that they are different subgroups of the same syndrome with different therapeutic targets, and different treatment and prognostic prediction strategies should be adopted [8, 9].
This investigation has numerous limitations that ought to be noted. Initially, because the trial was performed retrospectively, our team was not able to actively monitor TyG in patients during follow-up. Furthermore, due to the constraints that accompany single-center retrospective investigations with small sample sizes, we were unable to eliminate data bias, even after correcting several confounders. Thirdly, due to a lack of clinical information, variations in the prognosis of ADCHF between TyG and IR markers such as HOMA-IR and hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp were not explored further. Fourthly, the descriptions of ADCHF and DNHF may not be accurate. Insufficient details about patients who had previously received therapy or visited a nearby clinic would have influenced the diagnosis during admission. However, this limitation could be mitigated by gathering data from a relatively uniform sample in a tertiary hospital. Finally, to validate our findings, a prospective cohort study is required.
Conclusions
The research demonstrated that among non-diabetic patients, the TyG index was significantly associated with 5-year all-cause mortality in ADCHF patients but not in DNHF patients. Differentiating the predictive value of TyG between DNHF and ADCHF patients could enhance our understanding and refine treatment strategies for individuals with AHF.