Introduction
Heart valve surgery is associated with the risk of serious postoperative complications including death. One of the main causes of death in patients undergoing heart surgery is multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) due to irreversible perioperative cell damage [1, 2]. Glycolysis is the basic energetic process occurring in the cytoplasm of cells, including the brain, heart or skeletal muscle resulting in pyruvic acid. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate passes into the mitochondrion, where oxidative phosphorylation and the Krebs cycle allow generation of 36 moles of ATP. However, if the cells do receive a sufficient oxygen supply, their only source of energy is the energy-saving process of anaerobic glycolysis, whereby pyruvic acid with lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is converted to lactic acid, which at the physiological pH of the blood dissociates to the anionic base (lactate) and proton (H+) [3].
The correct concentration of bicarbonate ions, which are part of the body’s main buffer system (bicarbonate – carbonic acid), guarantees that there is no accumulation of hydrogen ions. However, if they are depleted and/or lactic acid is produced in excess and there are disturbances of its transformation or excretion, accumulating hydrogen ions cause a decrease in pH and development of lactic acidosis [4–6]. The usefulness of the lactate blood levels determined in the perioperative period as a predictor of death from all causes in patients undergoing heart valve surgery has not been fully explained.
Aim
Therefore, we attempted to evaluate the prognostic value of perioperative lactate blood levels during a 30-day follow-up for death in this group of patients.
Material and methods
This is a prospective study of consecutive patients with hemodynamically significant valvular heart disease (aortic stenosis, aortic regurgitation, mitral stenosis, mitral regurgitation) who were approved for cardiac surgery and subsequently underwent elective replacement or repair of the valve/valves, with or without additional procedures at the Institute of Cardiology, Warsaw, Poland. The exclusion criteria were: patients under 18 years of age, a lack of consent to participate in the study, porcelain aorta, active infective endocarditis and active neoplastic diseases. The day before surgery, immediately after the patient’s arrival at the intensive care clinic after surgery, 6 hours after the operation and one day after the operation (18 hours after the operation) a blood sample was collected from each patient. Complete blood count was performed with K2-EDTA samples, using a Cobas 6000 electronic counter (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). The plasma levels of lactate concentrations were measured by an electronic counter: the Cobas b 221 system (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). All procedures were performed through a midline sternotomy incision under general anaesthesia in normothermia. All patients were given cold blood cardioplegia at the initial dose of 15–20 ml/kg followed by booster doses of 5–10 ml/kg every 20 minutes. The primary end-point at the 30-day follow-up was death from all causes. Patients were followed by direct observation during hospitalization, clinic visits or telephone interview for 30 days after the surgery or until death. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SAS version 9.2 software. The Shapiro-Wilk test of normality was used to test the sample distribution. Data are presented as the mean ± SD and the frequency (%). Intergroup comparisons were made using the Mann-Whitney U test, Pearson’s χ2 test or Student’s t-test. The following covariates were investigated for association with the endpoint in univariate analysis: age, aortic cross-clamp time, cardiopulmonary bypass time, atrial fibrillation, body mass index, chronic obstructive airway disease, coronary artery disease, preoperative creatinine, creatinine measured one day before the operation, preoperative hemoglobin, hemoglobin measured one day before the operation, lac (lactates measured immediately after surgery), lac I (lactates measured 6 hours after the operation), lactates II (lactates measured 1 day after the operation (18 hours after operation)), pH (pH measured immediately after surgery), pH I (pH measured 6 hours after operation), pH II (pH measured one day after the operation (18 hours after the operation)), hypertension, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), New York Heart Association (NYHA) classes, platelets, pulmonary blood pressure, tricuspid annulus plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) and white blood cell count. Significant determinants (p < 0.05) identified from univariate analysis were subsequently entered into multivariate models. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was used to search for associations between the postoperative serum lactates level and selected variables. Predictive value of lactates was assessed by a comparison of the areas under the receiver operator characteristics of the respective curve. On the basis of the Youden index, a cut-off point was determined that met the criterion of maximum sensitivity and specificity for mortality prediction.
Results
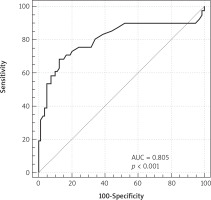
The study included 801 patients who underwent heart valve surgery with or without concomitant procedures. The mean age in the study group was 64.5 ±12.5. Thirty-three (4.3%) patients had significantly impaired left ventricular systolic function (ejection fraction ≤ 35%). The mean lac blood level was 1.7 mmol/l (standard deviation (SD) ± 0.4), lac I blood level was 2.2 ±1 mmol/l and lac II blood level was 2.6 ±2 mmol/l. Table I shows the characteristics of the patients studied. The primary end-point occurred in 36 patients. Total mortality was 4.4% versus 3.8% expected mortality calculated using EuroSCORE II. The first patient died suddenly (cause of death unknown) and 35 patients died during the follow-up period as a result of gradually increasing multi-organ failure. The statistically significant predictors of primary end point at univariate analysis are presented in Table II. At multivariate analysis lac II (OR = 1.413; 95% CI: 1.110–1.798; p = 0.004) and pH II (OR = 1.552; 95% CI: 1.146–2.102; p = 0.009) remained independent predictors of the primary end-point. The optimal cut-off point for death from all causes was calculated at 3.5 mmol/l lac II. The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve for primary end-point for lac II is 0.805 (95% CI: 0.721–0.870) (sensitivity: 75%; specificity: 82%) (Figure 1). A moderate correlation was found between the lac II blood level and preoperative hemoglobin (r = –0.31; p = 0.01), preoperative creatinine (r = 0.33; p = 0.002), preoperative RDW (r = 0.27; p = 0.04) and age (r = 0.21; p = 0.01), and also between lac I blood level and preoperative hemoglobin (r = –0.22; p = 0.02) as well as preoperative RDW (r = 0.17; p = 0.04). No correlation was found between the level of lac II and postoperative hemoglobin (p = 0.2), aortic cross-clamp time (p = 0.12) or cardiopulmonary bypass time (p = 0.15).
Table I
Baseline characteristics of study population
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Preoperative characteristics of patients (n = 801): | |
| Age [years]* | 63.1 ±12.9 |
| Male: men, n (%) | 461 (57) |
| Body mass index [kg/m2]* | 27.3 ±9.1 |
| NYHA, (classes)* | 2.6 ±0.5 |
| LV ejection fraction (%)* | 56 ±11 |
| EuroSCORE (%)* | 6.2 ±4.8 |
| EuroSCORE II (%)* | 3.8 ±3.4 |
| STS (%)* | 3.6 ±3.0 |
| Atrial fibrillation n (%) | 347 (43) |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 111 (13) |
| Chronic obstructive airways disease, n (%) | 52 (6) |
| Chronic kidney disease (GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m2), n (%) | 245 (30) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 133 (16) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 510 (63) |
| Peripheral atherosclerosis, n (%) | 43 (5) |
| Creatinine [mg/dl]* | 1 ±0.4 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dl]* | 13.5 ±1.5 |
| Intraoperative characteristics of patients: | |
| Aortic cross-clamp time [min]* | 94 ±40 |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass time [min]* | 122 ±53 |
| Postoperative characteristics of patients: | |
| Lactates [mmol/l]* | 1.7 ±0.4 |
| Lactates I [mmol/l]* | 2.2 ±1 |
| Lactates II [mmol/l]* | 2.6 ±2 |
| pH* | 7.4 ±0.07 |
| pH I* | 7.32 ±0.2 |
| pH II* | 7.34 ±0.1 |
| Creatinine II [mg/dl]* | 1.3 ±0.4 |
| Hemoglobin II [g/dl]* | 10.4 ±1.4 |
| Main procedures: | |
| AVR, n (%) | 401 (50) |
| AVP, n (%) | 30 (2.6) |
| MVR, n (%) | 161 (19.7) |
| MVR + AVR, n (%) | 60 (8.4) |
| MVP, n (%) | 149 (14.6) |
| Concomitant procedures: | |
| CABG, n (%) | 110 (13) |
AVP – aortic valve plasty, AVR – aortic valve replacement, MVP – mitral valve plasty, MVR – mitral valve replacement, GFR – glomerular filtration rate, LV – left ventricle, NYHA – New York Heart Association. Creatinine – creatinine measured one day before operation, Creatinine II – creatinine measured one day after operation (18 hours after operation), Hemoglobin – hemoglobin measured one day before operation, Hemoglobin II – hemoglobin measured one day after operation (18 hours after operation), Lactates – lactates measured immediately after operation, pH – pH measured immediately after operation, Lactates I – lactates measured 6 hours after operation, pH I – pH measured 6 hours after operation, Lactates II – lactates measured one day after operation (18 hours after operation), pH II – pH measured 1 day after operation (18 hours after operation).
Table II
Univariate analysis of predictive factors for occurrence of death
[i] Hemoglobin – hemoglobin measured 1 day before operation, Hemoglobin II – hemoglobin measured 1 day after operation (18 hours after operation), Lac I – lactates measured 6 hours after operation, Lac II – lactates measured 1 day after operation (18 hours after operation), pH II – pH measured 1 day after operation (18 hours after operation).
Discussion
The main cause of death in the early post-operative period in patients undergoing heart valve surgery is multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) [7, 8]. The pathophysiological basis for postoperative MODS is cellular damage, which is manifested when cellular repair does not occur. During operations the oxygen consumption is inadequate to meet intraoperative metabolic requirements [1, 2, 9, 10]. Hypoxia may result from insufficient blood supply caused by decreased cardiac output, reduced hemoglobin levels, or impaired absorption of oxygen by target cells. Determination of lactate blood level is helpful in diagnosis and assessment of hypoxia and lactic acidosis in people in shock or heart failure [11, 12]. In the present study, the authors assessed the usefulness of lactate concentration in successive perioperative measurements in terms of their predictive mortality in a 30-day follow-up. Under conditions of oxygen deprivation, anaerobic glycolysis is the only possible way to generate energy for the cell. In order to recover NAD+, the hydrogen atom is transferred from NADH to the pyruvic acid molecule to form a lactic acid molecule that dissociates to the anionic base (lactate) and proton (H+) at the physiological pH of the blood. So far, predictive ability of the lactate blood level was reported in patients requiring intensive therapy, especially in septic shock, with acute myocardial infarction, after liver transplantation or with bowel ischemia [13–21]. In turn, D’Arrigo et al. showed that lower lactate values were a predictor of a better prognosis after in-hospital cardiac arrest treated with extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation [22]. Moreover, Duval et al. suggest that changes in intraoperative blood lactate level (ΔLact) are associated with poor short-term outcomes in adult patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery [23].
On the other hand, O’Connor et al. proved that the discovery of late-onset hyperlactatemia should not delay the postoperative progress of cardiac surgery [11].
In the present study, among the three lactate blood levels evaluated, only the lactate blood level measured one day after the operation was an independent predictor of death in a 30-day follow-up. It is worth noting that in 35 cases out of all 36 deaths the cause of the primary endpoint was the increasing multi-organ failure. In the current literature, it has been shown that parameters of the red blood cell system such as erythrocytes and hemoglobin (which are indicative of the possibility of oxygen transport to tissues) or RDW (described as an indicator of the patient’s physiologic reserve) are independent predictors of death in patients undergoing heart surgery [24–29]. The significant correlation between lactate blood levels and preoperative parameters of the red blood cell system such as RDW or Hgb, demonstrated in this study, confirms the important role of perioperative tissue hypoxia in the development of postoperative complications.
Conclusions
In the present study lactate blood level measured one day after the operation was an independent predictor of death in a 30-day follow-up. The significant correlation between lactate blood levels and preoperative parameters of the red blood cell system confirms the important role of perioperative tissue hypoxia in the development of postoperative complications. The results of our research may be helpful in the perioperative strategy in patients undergoing heart valve surgery.