Introduction
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) refers to a series of symptoms and complications triggered via the reflux of duodenal and gastric contents into the esophagus, with the main clinical manifestations of acid reflux and heartburn [1]. Up to 1 billion people globally are demonstrated to be afflicted with GERD, with remarkable geographic variation [2], among which Latin America has the minimum prevalence at around 12.88% and North America has the maximum prevalence at about 19.55% [3]. Gradually, GERD has attracted a great deal of attention from clinicians, and the accurate diagnosis of various GERD phenotypes is one of the challenges faced by GERD patients. According to Rome IV, GERD phenotypes include non-erosive reflux disease (NERD), erosive reflux disease (ERD), reflux hypersensitivity (RH) and functional heartburn (FH) [4]. FH refers to a functional esophageal disorder [5] characterized by paroxysmal burning retrosternal discomfort or pain, with no evidence of mucosal histopathological abnormalities, GERD and major motility disorders or structural diseases, and for which adequate acid suppression therapy is ineffective [5]. Notably, it is clinically very similar to NERD as they both have heartburn as the main clinical symptom, and with no mucosal damage under white light endoscopy [6], which frequently need to be distinguished. Importantly, it has been proved that 24-h esophageal impedance-pH monitoring is a major means for identification of NERD and FH [7]. At present, researchers are attempting to identify and propose new impedance parameters to advance the differential diagnosis of FH and NERD [8]. Among them, mean nocturnal baseline impedance (MNBI) and the post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic wave (PSPW) index display good prospects in predicting the therapeutic response to acid-suppressing therapy, which may be helpful for identifying GERD phenotypes such as NERD, ERD, RH, and FH [9, 10]. MNBI is an impedance metric used to assess the integrity of the esophageal mucosa, which is calculated by evaluating the baseline impedance levels from the most distal channel (about 3, 5, 7, and 9 cm above the LES) at 3 time points during nighttime rest and taking the average value [11]. Research has demonstrated that NERD patients exhibited remarkedly lower distal MNBI versus FH patients [12]. On the other hand, PSPW is an index adopted for the evaluation of esophageal chemical clearance, which is expressed as the number of swallow-induced peristaltic wave reflux episodes within 30 s divided by the total number of reflux episodes [13]. It is also noteworthy that the esophageal clearance is intimately associated with the chemical clearance, mainly because bicarbonate in saliva that can neutralize gastric acid is transported to the distal esophagus through the swallow-induced peristaltic waves caused by esophago-salivary reflex, which benefits the repair of mucosal injury [13]. When esophagus pH is notably elevated, the esophago-salivary reflex is activated, suggesting that the swallowed bicarbonate-containing saliva has reached the distal esophagus [14]; when the PSPW index is diminished, it indicates dysfunction in esophageal chemical clearance, manifesting prolonged contact between esophageal mucosa and reflux, thus leading to heartburn symptoms [15, 16]. In comparison with healthy individuals, NERD patients exhibit a remarkably reduced PSPW index value [17], whereas FH patients have a normal PSPW index value [13]. In summary, we assumed that MNBI and the PSPW index are capable of distinguishing FH from NERD. Nevertheless, there have been no reports about it.
Aim
Accordingly, the purpose of this study was to explore the clinical value of MNBI and the PSPW index for making a distinction between FH and NERD.
Material and methods
Study subjects
A total of 128 patients with NERD and 105 patients with FH admitted to Taixing People's Hospital in the period from January 2020 to June 2023 were retrospectively and consecutively selected as the study subjects. Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 106 NERD patients (NERD group) and 82 FH patients (FH group) were ultimately enrolled. All patients underwent a complete physical examination including dietary habits, detailed medical history and the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Questionnaire (GERDQ). Also, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and 24-h multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH (MII-pH) monitoring in the esophagus were performed, and patients with esophageal motility disorders (including ineffective esophageal motility) were excluded based on the results of the high-resolution esophageal manometry system. Endoscopy was performed by 2 specialists who were unaware of the MII-pH monitoring results.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) 18–80 years old; 2) stopped proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or stopped prokinetic drugs for at least 2 weeks before MII-pH monitoring; 3) conformed to the corresponding diagnostic standards for NERD and FH patients; 4) had complete medical records; 5) had acid reflux or heartburn symptoms lasting more than 6 months, at least 3 times a week, and with negative endoscopic examination.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) RH, eosinophilic esophagitis, connective tissue disease; 2) outflow tract obstruction; 3) history of excessive alcohol consumption, gastrointestinal surgery, cancer, esophageal motility disorders, esophageal varices, stroke, severe neurological disorders, or disorders of the ear, nose, and throat system; 4) incomplete medical records.
Diagnostic criteria
1) NERD: Based on the Lyon Consensus and the Rome IV diagnostic standards, the NERD group was defined as patients with negative endoscopic findings, abnormal AET (> 6%), symptom index (SI) ≥ 50% and/or symptom association probability (SAP) ≥ 95% (symptom-reflux correlations), and response to PPI treatment (symptomatic improvement score ≥ 50%).
2) FH: Based on the Lyon Consensus and the Rome IV diagnostic standards, the FH group was considered as patients who had endoscopically complete esophageal mucosa with normal esophageal acid exposure during 24-h MII-pH monitoring, no correlation between symptoms and reflux, and no response to PPI treatment (symptomatic improvement score < 50%). AET < 4% of pH < 4 in 24-hour MII-pH monitoring was considered as normal acid exposure. SAP < 95% and SI < 50% were viewed as equivalent to having no symptoms correlated with reflux.
Treatment regimen
After the survey, all patients underwent 8-week PPI treatment, and based on response to PPIs, the GERD phenotype was determined. According to data from the GERDQ, response to PPI treatment was defined as at least 50% improvement in esophageal reflux symptoms during evaluation. Patients with indefinite GERD outcomes were excluded on the basis of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, MII-pH value, or response to PPI therapy.
Medical record collection
Outpatient medical records were collected retrospectively from all the subjects by reviewing the medical records, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), occurrence of major clinical symptoms (heartburn, chest pain, reflux, burning sensation in the throat, belching, postprandial fullness, and burning sensation in the epigastrium), AET, low esophageal sphincter (LES) tone, bolus clearance time (BCT), total reflux episodes, acid reflux episodes, and non-acid reflux episodes.
24-hour MII-pH monitoring
All subjects were supposed to stop PPI or prokinetic drug treatment at least 2 weeks before MII-pH monitoring. Prior to impedance-pH monitoring, standard esophageal manometry was routinely conducted for locating the LES using the station pull-through method, and acquiring the mean LES tone, distal contractile integral (DCI), contractile front velocity (CFV), and integrated relaxation pressure (IRP) [18–20]. A PVC catheter assembly with a diameter of 2.3 mm was utilized to record MII-pH comprising a series of impedance electrodes, with an axial length of 4 mm and an interval of 2 cm each, as well as a distal-pH electrode (Sandhill Scientific, Highland Ranch, CO, USA). Before MII-pH monitoring, the pH electrodes were calibrated utilizing pH 4.0 and pH 7.0 buffer solutions. After pressure measurement and localization by high resolution manometry, the patient’s nose was anesthetized by a clinician, with a pH-impedance catheter nasally inserted into the esophagus and secured to the nasal wing with adhesive tape. The pH sensor and impedance electrodes were both located about 5 cm from the LES, and the 24-hour pH-impedance changes were recorded utilizing a recorder.
Intracavity impedance and pH data analysis
The following variables were collected through reviewing the medical records: (1) episodes and type of reflux episodes; (2) AET; (3) MNBI value; (4) PSPW value. Among them, reflux episodes were allocated into acid reflux (pH < 4.0) and non-acid reflux (pH > 4.0); (5) The median BCT, and the SAP and the SI were also calculated utilizing the BioView Analysis software. A positive SAP was defined by ≥ 95% of symptoms related to reflux, and a positive SI was defined by ≥ 50% of symptoms related to reflux [21].
The MNBI level was evaluated by a researcher who did not know the diagnostic results for 10 min each time point at 1 a.m., 2 a.m., and 3 a.m. MNBI was the average of the baseline impedance levels during these three time periods. This study selected the z5 impedance channel (5 cm from from LES) to evaluate the MNBI level. PSPW was defined as the occurrence of an antegrade 50.0% drop after a reflux event within 30 s, which originated from the most proximal impedance channel to all remaining distal impedance channels, followed by ≥ 50.0% return to the baseline. The PSPW index was determined when dividing the PSPW episodes by the total reflux events.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis and plotting were conducted using SPSS 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and GraphPad Prism 8.01 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) software. The Shapiro-Wilk test method was used for normal distribution testing. The measurement data of normal distribution were represented by mean ± standard deviation, and the independent sample t-test was used between two groups. The non-normally distributed measurement data were represented by the median (minimum, maximum), with the Mann-Whitney test used between two groups, and Spearman correlation coefficient analysis used for analyses of the correlations between various indicators. The classification variables were represented by the episodes of examples (%) and were tested using the χ2 test. Logistic multivariate regression analysis was used to identify the independent influencing factors of NERD and FH. The diagnostic value of MNBI and the PSPW index in distinguishing FH from NERD was analyzed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. P was a bilateral test, and p < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
Results
Comparisons of clinical baseline characteristics
On the basis of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 106 NERD patients and 82 FH patients were selected as the study subjects. The two groups of patients had no significant differences in age, sex, clinical symptoms (heartburn, chest pain, reflux, burning sensation in the throat, belching, postprandial fullness, and burning sensation in the epigastrium), BMI, BCT, DCI, CFV, IRP indicator, and GERDQ score (all p > 0.05), indicating comparability of the data. However, the two groups differed significantly in terms of LES tone, AET, total reflux episodes, acid reflux episodes, and episodes of non-acid reflux (all p < 0.001) (Table I).
Table I
Comparisons of clinical baseline characteristics
[i] BMI – body mass index, AET – acid exposure time, LES – low esophageal sphincter, BCT – bolus clearance time, DCI – distal contractile integral, CFV – contractile front velocity, IRP – integrated relaxation pressure. The measurement data of normal distribution were represented as mean ± standard deviation, with the independent sample t-test adopted for comparisons between two groups. The non-normally distributed measurement data were represented by the median (minimum, maximum), and the Mann-Whitney test was utilized for comparisons between two groups. The categorical variables were compared and analyzed using the χ2 test. P < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
Comparisons of MNBI and PSPW index between NERD and FH patients
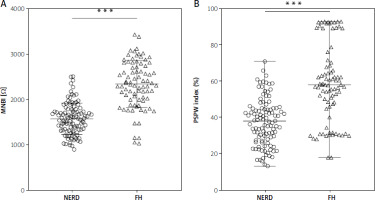
To analyze the differences in MNBI and the PSPW index between NERD and FH patients, MNBI and PSPW levels were monitored by means of 24-hour MII-pH and calculated. As reflected by the results, the MNBI and PSPW index levels in the NERD group were significantly lower versus the FH group (Figures 1 A, B, all p < 0.001).
Figure 1
A – MNBI levels in NERD and FH patients; B – PSPW index levels in NERD and FH patients. The measurement data in panel (A) were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, followed by independent sample t-tests for comparisons between two groups. The measurement data in panel (B) were represented by the median (minimum, maximum), with the Mann-Whitney test used for comparisons between two groups. ***P < 0.001
Correlation analysis of MNBI and PSPW with pathological indicators in subjects
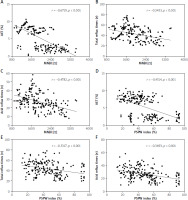
To clarify the relationship between MNBI and PSPW index and all subjects’ (NERD and FH patients) pathological indicators (AET, total reflux episodes, and acid reflux episodes), Spearman analysis was employed for investigating their correlations. The level of MNBI had significantly negative correlations with AET (r = –0.6719, p < 0.001), acid reflux episodes (r = –0.4782, p < 0.001), and total reflux episodes (r = –0.3453, p < 0.001) (Figures 2 A–C). The level of PSPW had significantly negative correlations with AET (r = –0.4514, p < 0.001), acid reflux episodes (r = –0.3693, p < 0.001), and total reflux episodes (r = –0.3317, p < 0.001) (Figures 2 D–F).
Figure 2
Spearman analysis was performed on the correlations of MNBI with AET (A), total reflux episodes (B) and acid reflux episodes (C); Spearman analysis was conducted on the correlations of PSPW index with AET (D), total reflux episodes (E) and acid reflux episodes (F). r was the correlation coefficient, and p < 0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant
MNBI and PSPW index were independent influencing factors for differentiating NERD and FH
To exclude confounding factors, FH was viewed as the independent variable and MNBI, LES tone, PSPW, BCT, total reflux episodes, and acid reflux episodes were considered as the dependent variables in a logistic multivariate regression analysis. The results suggested that MNBI, LES tone, PSPW, total reflux episodes, and acid reflux episodes were independent influencing factors for identifying NERD and FH (Table II).
Table II
MNBI and PSPW index were independent influencing factors for discriminating NERD from FH
MNBI and PSPW index could assist in identifying NERD and FH
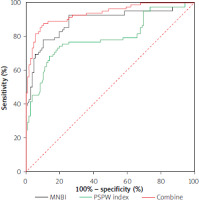
To probe into the diagnostic value of MNBI and the PSPW index for distinguishing NERD from FH patients, ROC curve analysis was conducted, with FH regarded as the state variable and MNBI and PSPW values as test variables. Both MNBI > 1975 and PSPW > 47.12 had high value for the differential diagnosis of NERD and FH (Table III, Figure 3). Finally, the combination analysis of ROC curves was performed on the diagnostic value of MNBI and PSPW for identifying NERD and FH patients. The combined detection of MNBI and PSPW had high application value for the differential diagnosis of NERD and FH (area under the curve = 0.934, 0.43 cut-off value, 87.8% sensitivity, 89.62% specificity) (Table III, Figure 3, all p < 0.05) and was superior to MNBI and PSPW stand-alone detection. The above results suggested that MNBI and the PSPW index were both helpful to distinguish NERD from FH, and the combinative diagnostic value of the two was even higher.
Table III
Combined analysis of ROC curve on the diagnostic value of MNBI and PSPW index for distinguishing NERD patients from FH patients
| Variable | AUC | 95% CI | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Cutoff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNBI | 0.889 | 0.835–0.930 | 78.05 | 89.62 | 1975 |
| PSPW index | 0.792 | 0.726–0.847 | 74.39 | 80.19 | 47.12 |
| Combine | 0.934 | 0.889–0.965 | 87.8 | 89.62 | 0.43 |
| Pa | p = 0.003 | ||||
| Pb | p < 0.001 | ||||
Discussion
The global prevalence of GERD remains high, and is constantly increasing [22]. NERD patients are a heterogeneous group comprising a variety of subpopulations with distinct mechanisms for their major symptom of heartburn, whereas an additional group is called FH patients, because this typical symptom is linked neither to a positive symptom index nor to an abnormal pH test, with their response to PPIs very disappointing [23], which highlights the importance of their differentiation for better treatment. Evidence has shown that a clear distinction between NERD and FH is actually possible through the use of impedance-pH monitoring [24]. Notably, the PSPW index and MNBI level are reported to be able to enhance the diagnostic value of 24-hour MII-pH monitoring in GERD individuals [12]. Thus, we assumed that they play roles in differentiating NERD from FH and investigated it, and our findings highlighted that MNBI and PSPW were independent risk factors for NERD and FH, and they had high value for the differential diagnosis of NERD and FH.
Reportedly, it is difficult to distinguish patients diagnosed with NERD and those with FH despite their highly clinically relevance: the former group mostly benefits from surgical anti-reflux therapy or from pharmacological suppression of acid secretion, while in the latter group, long-lasting treatment with anti-reflux surgery and PPI are unnecessary and possibly hazardous and should be completely avoided [25]. NERD is further defined by abnormal AET (% pH < 4.0 ≥ 6), while patients are defined as FH via normal endoscopy and normal AET (% pH < 4.0 < 6) [26]. NERD patients have more episodes of reflux events (86 ±33.4) and a higher mean AET (6.3 ±4.8) relative to FH patients (AET 0.5 ±0.6; reflux events 24.6 ±7.9) [27]. Not surprisingly, our results also reflected the fact that there were obvious differences in AET, LES tone, total reflux episodes, acid reflux episodes, and episodes of non-acid reflux between NERD patients and FH patients.
Previous research illustrated that MNBI is associated with esophageal histopathologic changes and is lower in GERD individuals than in healthy subjects and FH individuals [28, 29]. The PSPW index, which can be used to evaluate the impaired chemical clearance in GERD patients, is notably lower in NERD patients than in those with FH [13]. Consistently, our results demonstrated lower MNBI and PSPW values in the NERD group than the FH group. MNBI has a remarkably negative correlation with total reflux episodes and AET 4%, with a high diagnostic value in differentiating conclusive GERD [30]. We investigated the correlations of MNBI and PSPW values with pathological indicators of patients, and also discovered negative correlations of the MNBI and PSPW values with AET and total and acid reflux episodes.
Furthermore, distal MNBI is a good way to diagnose GERD phenotypes [31]. Research has demonstrated that MNBI and the PSPW index have potential to be part of the standard analysis of impedance-pH tracings for diagnosing GERD in individuals with endoscopy-negative heartburn [32]. The PSPW index and MNBI are proved to increase the diagnostic accuracy of MII-pH monitoring in patients with PPI responsive heartburn [17]. The PSPW index and MNBI in distal esophageal are capable of elevating the diagnostic value of MII/pH for identifying Chinese heartburn patients in particular [33]. Under impedance-pH monitoring in therapy, it is also noteworthy that MNBI and PSPW are reproducible and highly applicable, and their calculation only needs a few extra minutes when impedance-pH tracings are manually reviewed [32]. Importantly, both MNBI and the PSPW index are able to distinguish FH from NERD patients, and MNBI may be more valid than the PSPW index [12]. MNBI and PSPW index effectively segregate FH from PPI-refractory NERD [34]. All of these reports have evidenced MNBI and PSPW as a potential tool to be used for FH and NERD differentiation, and our findings revealed that MNBI and PSPW index assisted in the discrimination of NERD and FH, with their combination showing higher clinical application value. In addition, MNBI and the PSPW index, number of episodes of total reflux and acid reflux, and LES tone were independent risk factors for segregating NERD from FH.
Conclusions
This study revealed that MNBI and PSPW were independent risk factors for the occurrence of NERD, and MNBI and the PSPW index could be used to distinguish NERD from FH. However, PSPW was defined as the occurrence of an antegrade 50.0% drop after a reflux event within 30 s, originating from the most proximal impedance channel to all the remaining distal impedance channels, and followed by ≥ 50.0% return to the baseline. The PSPW index was assessed when dividing the number of PSPW episodes by the total reflux events. The calculation of the PSPW is manual and still requires more time and experience than the MNBI. Moreover, the number of cases and events included in the study is relatively small, and further expansion of sample size and multi-center research are needed to increase the credibility of results. Furthermore, relevant studies are only conducted on NERD and FH patients, and further analysis on the relevant indicators inducing NERD and FH is needed, in an effort to provide a more convenient and accurate way to identify NERD from FH.