INTRODUCTION
Psoriasis is a persistent, immune-mediated inflammatory skin disease that affects approximately 2–3% of the global population. It is often associated with significant comorbidities, including cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorder [1]. The development of psoriasis results from complex genetic, immune, and environmental interactions that lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of keratinocytes and chronic inflammation. It is characterized by the activation of the IL-23/Th17 axis, which play a vital role in driving the inflammatory response seen in psoriatic lesions [2]. This immune dysregulation is further exacerbated by oxidative stress and altered metabolic pathways that play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology [3]. Additionally, genetic studies have identified key susceptibility loci, especially in the MHC region, contributing to the understanding of psoriasis genetics [4].
Interleukin-37 (IL-37), an anti-inflammatory cytokine, is significantly downregulated in psoriatic lesions, which may contribute to the excessive inflammatory response observed in psoriasis [5]. Research indicates that IL-37-producing immune cells, including CD4+ T cells and macrophages, are elevated in psoriatic lesions despite the overall decrease in IL-37 gene expression [6].
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a key factor in angiogenesis, is found at elevated levels in the serum of psoriasis patients, with its concentration correlates with disease severity [7]. IL-37 has been shown to suppress the inflammatory process in psoriasis models by reducing keratinocyte hyperproliferation and cytokine production [8]. VEGF also plays a role in recruiting inflammatory immune cells, including γδ T cells, which further exacerbate psoriatic inflammation [9]. Studies suggest that VEGF-induced angiogenesis and inflammation contribute to psoriatic lesion persistence and treatment resistance [10]. Systemic blockade of VEGF has demonstrated promising results in reducing psoriatic skin inflammation and lesion severity [11]. IL-37 also interacts with VEGF pathways, potentially modulating the angiogenic and inflammatory responses in psoriasis [6]. New therapeutic approaches are being explored that target both IL-37 and VEGF to control psoriasis-associated inflammation and vascularization [12]. These findings highlight the crucial roles of IL-37 and VEGF in psoriasis pathogenesis and suggest potential targets for innovative treatment strategies [8].
AIM
In this study, the primary objective was to evaluate the levels of IL-37 and VEGF in psoriasis patients and compare them with healthy control subjects. The study aimed to determine if these biomarkers, known for their roles in inflammation and vascularity, were differentially expressed in patients with psoriasis compared to controls.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
STUDY DESIGN AND POPULATION
This is a case-control study including 50 psoriasis patients and 50 healthy volunteers as controls. The psoriasis diagnosis was determined based on clinical and dermoscopic examination; meanwhile, a skin biopsy was performed if the diagnosis was uncertain. Exclusion criteria included having pustular or erythrodermic psoriasis, having psoriatic arthritis, receiving local or systemic treatment within the previous 3 months, having any other skin or systemic disorders, and being a pregnant or lactating female.
SAMPLE COLLECTION
One hundred samples were collected, ranging in age from 10 to 60 years, of both sexes, who visited Al-Hillah Teaching Hospital during the period from August 2024 to January 2025. Fifty samples were from patients with psoriasis and fifty were from healthy people who did not have any medical history or clinical signs of other diseases. All patients were diagnosed by a dermatologist.
MEASUREMENT OF PASI SCORE
To appreciation the severity of psoriasis, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score was used. The PASI score is a widely recognized assessment tool that evaluates the extent and severity of psoriasis lesions considering the percentage of body surface area (BSA) affected along with severity of erythema, infiltration, and desquamation accross different body regions (head, upper limbs, trunk, and lower limbs). The PASI score ranges from 0 to 72 points, with higher values indicating more severe disease.
PASI SCORING CATEGORIES
The PASI score was categorized into three disease severity levels: mild disease: PASI score < 7, moderate disease: PASI score between 7 and 15, severe disease: PASI score > 15.
MEASUREMENT OF SERUM LEVELS OF IL-37 AND VEGF
Five milliliters of blood were taken from each subject, and 2 ml of serum were recovered by centrifugation at 8000 rpm/10 min. Serum concentrations of VEGF and IL-37 were determined using ELISA. After the determination of diluted standard, blank, and sample wells, 100 μl of each dilution were added, and the micro-ELISA plate was covered by the sealer and incubated for 90 min at 37ºC. After incubation, all liquid was taken out from each well, 100 μl of biotinylated detection antibody solution were added to each well, and the micro-plate was covered with a new sealer and incubated for 1 h at 37ºC. After incubation, all liquid was taken out from each well and washed by adding 350 μl of washing buffer to each well (these steps were repeated 3 times). 100 μl of HRP conjugate working solution were added to each well, covered by a micro-plate and incubated at 37ºC for 30 min. The solution was removed from each well, and the washing step was repeated 5 times. Then 90 μl of the substrate reagent were added to each well, and the micro-plate was covered by the micro-plate sealer and incubated for 15 min at 37ºC. 50 μl of the stop solution were added to each well, and determination of the optical density (OD value) was done by ELISA reader at 450 nm wavelength, then the results were calculated by plotting the standard curve.
RESULTS
Demographic characteristics of the study population were similar between the psoriasis group and the control group (Table 1). The psoriasis group consisted of 39.4 ±12.3-year-old participants, and the control group contained 38.8 ±12.7-year-old participants. The two groups were found to have the same age distribution using the independent t test with the p-value of 0.815, which indicated no significant difference. Regarding gender distribution, the psoriasis group comprised 35 (70%) females and 15 (30%) males, while the control group included 33 (66%) females and 17 (34%) males. The χ2 test demonstrated no statistically significant difference in gender distribution between the groups (p = 0.327) shown in Table 1. Duration disease ranged from 1 to 24 years. The mean PASI score was 14.88 ±7.54 and ranged from 2 to 33.8. According to the PASI score, psoriasis severity was mild in 12 (24 %) patients, moderate in 15 (30 %), and severe in 23 (46%) patients.
Table 1
Demographic characteristics comparison between psoriasis and control groups
| Characteristic | Psoriasis group (n = 50) | Control group (n = 50) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 39.4 ±12.3 | 38.8 ±12.7 | 0.815 | |
| Gender | 0.327 | |||
| Female | 35 (70%) | 33 (66%) | ||
| Male | 15 (30%) | 17 (34%) | ||
SERUM LEVEL OF IL-37 AND VEGF
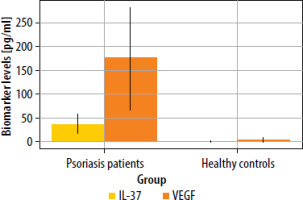
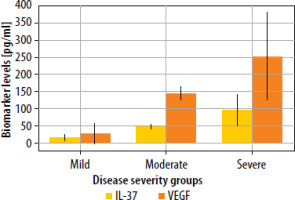
The statistical analysis revealed significant differences in IL-37 levels between psoriasis patients and healthy controls (p < 0.001). Among psoriasis patients (n = 50), the mean IL-37 level was approximately 36.86 ±19.72 pg/ml, with a median value of 35 pg/ml and a range from 5.80 pg/ml to 72 pg/ml. In contrast, healthy controls (n = 50) exhibited markedly lower IL-37 levels, with a mean of 0.36 ±0.25 pg/ml, a median of 0.30 pg/ml, and values ranging from 0.10 pg/ml to 0.90 pg/ml. Similarly, VEGF levels were significantly elevated in psoriasis patients compared to healthy controls (p < 0.001). The mean VEGF concentration in psoriasis patients was approximately 176.41 ±106.21 pg/ml, with a median value of 164 pg/ml and a wide range from 3.70 pg/ml to 669 pg/ml. In contrast, healthy controls had much lower VEGF levels, with a mean of 3.62 ±4.36 pg/ml, a median of 1.90 pg/ml, and values ranging from 0.10 pg/ml to 17 pg/ml (Table 2, Figure 1). Moreover, IL-37 concentrations were significantly higher in cases with severe disease than in cases with mild or moderate disease. The analysis of VEGF and IL-37 levels across different disease severity groups revealed significant variations. VEGF levels demonstrated a clear stepwise increase corresponding to disease severity, with the mild group showing the lowest concentration (mean: 26.06 ±29.92 pg/ml), followed by a substantial increase in the moderate group (mean: 143.36 ±19.95 pg/ml), and reaching the highest levels in the severe group (mean: 252.93 ±129.38 pg/ml). The difference between these groups was statistically significant (p < 0.001), indicating a strong association between VEGF expression and disease progression. The wide range observed in the severe group (149.90–669.00 pg/ml) suggests considerable variability in VEGF expression among patients with severe disease, possibly reflecting different pathophysiological mechanisms or disease stages. Similarly, IL-37 levels exhibited a comparable pattern of elevation with increasing disease severity. The mild group had the lowest IL-37 concentration (mean: 14.48 ±8.27 pg/ml), while the moderate group showed intermediate levels (mean: 47.07 ±8.67 pg/ml), and the severe group demonstrated the highest values (mean: 95.25 ±45.77 pg/ml) (Table 3, Figure 2).
Table 2
Statistical comparison of IL-37 and VEGF levels between psoriasis patients and healthy controls
Table 3
Statistical comparison of IL-37 and VEGF levels across disease severity groups. Statistically significant at p < 0.05
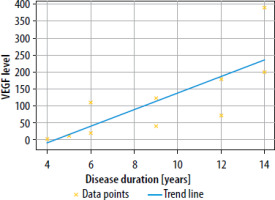
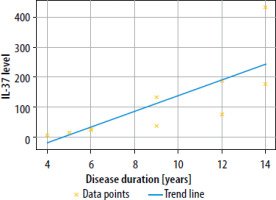
The analysis of the relationship between IL-37 and VEGF levels across different disease duration groups revealed interesting patterns of correlation. Overall, there was a very strong positive correlation between IL-37 and VEGF levels when all groups were combined (r = 0.891, p < 0.001), indicating that as disease duration increased, both biomarkers showed a consistent pattern of elevation (Figures 3, 4).
DISCUSSION
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characteristized by distinct histological changes, including abnormal epidermal proliferation [13]. The varying levels of inflammatory cytokines observed across different morphological phenotypes of psoriasis, despite similar disease duration may provide a partial explanation for the conflicting results regarding cytokine levels reported previously. This suggests that both the IL-37 and VEGF pathways play a role in the pathogenesis psoriasis.
In the current work, the relationship between IL-37 and VEGF in psoriasis development was evaluated by measuring their serum concentrations in psoriasis patients in comparison to healthy controls. In psoriatic patients, we detected significantly higher serum IL-37 levels compared to controls. This is concordant with [14] and [15] who found IL-37 was elevated in skin lesions of psoriasis patients compared to controls and had been recognized as a vital factor for inflammation in PsO. Similarly, Wulamujiang et al. [6] showed that IL-37 producing tissue resident immune cells were significantly elevated in psoriatic lesions, which supports the notion that IL-37 might contribute to psoriasis pathogenesis. On the contrary, Słucznowska-Głabowska et al. [16] detected a lower IL-37 level in serum of psoriatic cases than healthy controls, but this was not statistically significant (p = 0.125). The fact that all cases in their study had mild to moderate disease may be the cause for the variation between the two studies. In our work, IL-37 level showed a significant direct correlation with PASI score in psoriatic cases. Additionally, patients with severe psoriasis showed significantly higher serum levels of IL-37 than cases with mild or moderate disease, suggesting a potential involvement of IL-37 in psoriasis severity [17]. Similarly, with Tsuji et al. in 2023 who found a correlation between serum levels of IL-37 and psoriasis severity has been demonstrated; it appears that IL-37 may counteract for the inflammatory effects of IL-33 potentially by inhibiting MAPK and STAT1 activation in human keratinocytes, to improving skin function of patients and enhancing disease prognosis [18]. Furthermore, our research revealed a significant positive correlation between the IL-37 level and disease duration, suggesting the possible implication of IL-37 in disease chronicity [19]. In the present study, psoriatic patients demonstrated significantly higher serum concentrations of VEGF than the control group. This observation is consistent with previous studies [20, 21] and supports the crucial role of VEGF in psoriasis development. We detected a significant direct relationship between serum VEGF level and psoriasis severity, measured by the PASI score. Furthermore, VEGF levels were significantly higher in cases with severe psoriasis compared to cases with mild or moderate psoriasis. Our results were in agreement with those reported by Sobolev et al. [22]. In the present work, psoriatic patients demonstrated a significant direct correlation between serum VEGF level and disease duration, supporting the potential role of VEGF in psoriasis chronicity. Our findings were in agreement with those reported by Du et al. [23].
CONCLUSIONS
Through the study, it was demonstrated that psoriasis patients had significant elevation of both IL -37 and VEGF levels compared to healthy controls. They were also found to correlate with the severity of the disease, which may make these biomarkers useful to indicate progression of the disease. The pathophysiology of psoriasis includes both IL-37 which is anti-inflammatory, and VEGF which is a major mediator of angiogenesis. Overall, these findings suggest that targeting IL-37 and VEGF could yield novel therapeutic strategies for managing psoriasis or are likely to provide useful insights for developing such biomarkers.