INTRODUCTION
Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated disease with an estimated prevalence of 2–4% of Western populations, characterized by the occurrence of symmetrical, well-demarcated erythematous plaques with silver scales [1]. It has been associated with multiple comorbidities including cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, psychological and psychiatric disorders [2]. Furthermore, psoriatic arthritis may occur in about 20% of patients with psoriasis [3]. The pathophysiology of psoriatic disease is known to be multifactorial, involving genetic associations, environmental factors, skin barrier dysfunction and dysregulated inflammation [4]. The first-line treatment for the patients with mild psoriasis is topical treatment [5]. Patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis require phototherapy, non-biologic systemic therapies (methotrexate, acitretin, cyclosporine A, fumaric acid esters) or biologic agents [6].
Over the past several years, substantial improvements in comprehending the pathophysiology of psoriasis have led to the development of novel potential therapeutic targets and drugs. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are small-molecule drugs that act by blocking one or more of the intracellular tyrosine kinases: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2. Suppression of the intracellular signal pathway mediated by JAK and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins, inhibits gene transcription of proinflammatory cytokines [7].
The majority of the inflammatory pathways associated with psoriasis involve cytokines and growth factors that are mediated through receptors linked to Janus kinases [8]. JAK inhibitors have recently become a new treatment strategy for managing psoriatic disease. Tofacitinib (preferential JAK1 and JAK3 inhibitor) and upadacitinib (JAK1 inhibitor) have been approved for psoriatic arthritis, and deucravacitinib (TYK2 inhibitor) for plaque psoriasis [9]. The growing evidence suggests that JAK inhibitors are a promising and well-tolerated alternative for patients whose disease cannot be adequately managed with conventional or biologic therapies [10]. Nevertheless, their safety profile has recently been the subject of serious concern, particularly in reference to therapy-induced immunosuppression, carcinogenesis and subsequent development of skin malignancies.
Patients with psoriasis are more likely to develop non-melanoma skin cancer, specifically squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), because of their previous exposure to PUVA and immunosuppressants, including cyclosporine A and possibly methotrexate [11–13]. TNF-a inhibitors may increase the risk of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) [14, 15]. According to some research, patients treated with JAK inhibitors, especially with tofacitinib and ruxolitinib, are more likely to develop malignancy, particularly NMSC. This risk may be comparable to the general population in patients with dermatological conditions like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and atopic dermatitis [16].
Recently we published a review concerning the role of interleukin-12, -23, and -17 in the development of skin malignancies, showing conflicting results regarding their role as either promotors or inhibitors of tumor development [17]. Here, we aimed to investigate the significance of the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathway in the carcinogenesis, with a particular focus on skin neoplasms, and to gather the data on safety of JAK inhibitors regarding the risk of melanoma and NMSC.
THE ROLE OF THE JAK/STAT PATHWAY IN THE TUMORIGENESIS
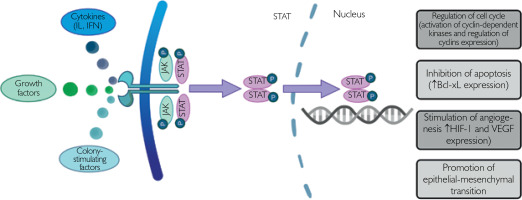
The JAK/STAT signaling pathway is considered one the most pivotal links in intracellular signaling, since it enables proper membrane-to-cell signal transduction. It is made up of four non-receptor tyrosine protein kinases (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2) and seven STATs (STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5a, STAT5b, and STAT6), constituting the JAK and STAT family, respectively [18]. All JAK family members are expressed in most of human tissues, apart from JAK3, which is expressed exclusively in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, in the lymphatic system and the bone marrow [18]. Each JAK protein exerts diverse functions and is associated with different cytokine receptors. Activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway starts with binding of cytokines (interleukins, interferons (IFN), growth factors, colony-stimulating factors) to their cell membrane receptors, what leads to the phosphorylation of the associated JAK protein. In the next stage STAT proteins are phosphorylated by tyrosine, form homodimers or heterodimers, enter the nucleus and activate transcription processes [18–20].
To date, many research papers have provided evidence that activation of STAT proteins lead to the development and progression of solid tumors and hematologic neoplasms, associated with poor prognosis [21, 22]. Therefore, the inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway has been a matter of interest in terms of tumorigenesis and potential anti-cancer action. The role of JAK/STAT activation is essential in classical myeloproliferative malignancies such as polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis, which are linked to the gain-of-function mutation in the JAK2 gene (JAK2 V617F) and other direct and indirect mechanisms of JAK/STAT pathway activation [23, 24]. In 2011, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor, to treat myelofibrosis and afterwards polycythemia vera and graft-versus-host disease [24]. Ruxolitinib has emerged as a potent therapeutic agent since then and been shown to improve sensitivity to other conventional or targeted agents [21].
The exact mechanism in which JAK/STAT signaling contributes to cancer cell proliferation and growth is not completely understood [22]. Mutations leading to STAT3 hyperactivation are commonly found in large granular lymphocytic leukemia, which indicates the role of STAT3 in the pathogenesis of this malignancy [25]. In glioblastoma, loss of protein inhibitors of activated STATs (PIAS) proteins with enhanced STAT3 signaling was observed [26]. In prostate cancer, activation of the STAT protein was found to be mediated by interleukin-6 binding to the gp130 receptor [27]. STAT activation in cancer drives cell division and growth and inhibits apoptosis by regulating transcription of cyclins and the anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) [22]. STAT3 activates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1) target genes and thus promotes tumorigenesis under hypoxic conditions [28]. Moreover, it induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by increasing TGF-β1-induced TWIST1 expression and thereby stimulates progression of prostate cancer [29]. The procarcinogenic effect of the JAK/STAT pathway has been summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Proposed model of the procarcinogenic role of the JAK/STAT pathway. Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway drives cell division and growth and inhibits apoptosis by regulating the expression of cyclin-dependent kinases, cyclins and anti-apoptotic proteins. Moreover, pro-tumorigenic effects are associated with enhanced angiogenesis and promotion of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Contrary, there is some evidence on the anti-carcinogenic effect of JAK/STAT signaling. For example, STAT1 has been found to serve a protective function by enhancing pro-apoptotic effect [30]. Additionally, TYK2-deficient mice were more likely to develop Abelson-induced B lymphoid leukemia/lymphoma as well as TEL-JAK2–induced T lymphoid leukemia than controls [31]. Similarly, JAK1 is shown to play a tumor-suppressing role in Abelson-transformed pro-B cells by enhancing IFN-γ-dependent apoptosis [32]. Ectopic expression of microRNA (miR)-214 in lung cancer cell lines inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells by reducing the expression of JAK1 [33].
In recent years, multiple studies aimed to investigate the relationship between expression of different components of the JAK/STAT pathway and the prognosis of various malignancies. Increased STAT1 expression was found to be correlated with better prognosis in patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer [34] and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [35], and with poor prognosis in patients with lung, ovarian, gastric, blood, brain cancers [36] and breast cancer [37]. On the other hand, STAT3 was associated with the advanced TNM stage or poor prognosis in gastric cancer, osteosarcoma and high-grade serous carcinoma [38–40].
THE ROLE OF THE JAK/STAT PATHWAY IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF SKIN NEOPLASMS
Melanoma
The action of STAT3 protein has been widely investigated in in vitro, in vivo, and animal models of melanoma. In a study conducted by Messina et al. [41], the expression of phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3), phosphorylated STAT1 (pSTAT1) and interferon-α receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR-1) was analyzed in different types of nevi (compound, dysplastic, congenital), melanoma and lymph node metastasis. The results showed that benign melanocytic nevi presented no significant staining of IFNAR-1, pSTAT1, or pSTAT3, whereas high levels of either pSTAT1 or pSTAT3, as well as IFNAR-1 staining were observed in melanoma and lymph node metastases. Thus, increased STAT3 signaling was found in melanoma, but not in benign melanocytic nevi [41]. Additionally, a higher recurrence rate was observed in patients with greater pSTAT3 levels than with lower pSTAT3 levels, while higher pSTAT1 levels were associated to the lower recurrence rate than in patients with weak or absent pSTAT1 [41]. According to Hu et al. [42], melanoma tissues were characterized by the significantly decreased E-cadherin expression, while the levels of CXCL8, JAK2, STAT3, vimentin, and N-cadherin were notably increased, indicating that the inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling and subsequent apoptosis of melanoma cells and inhibition of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition can be achieved by silencing of CXCL8 gene expression [42]. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling with a dominant-negative STAT3 led to the apoptosis of B16 mouse melanoma cells [43]. In addition, targeting STAT3 inhibits hypoxia inducible factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, thereby blocking cell proliferation and angiogenesis [44]. STAT3 has also been found to act as a regulator of the BRAFV600E signaling, which drives Mcl-1 transcription factor in response to BRAF signaling, and, thus, contributes to melanoma cell proliferation and survival, as well as chemoresistance of BRAFV600E melanoma [45]. Due to this fact, STAT3 targeted therapies emerge in in vitro studies as novel therapeutics able to overcome the resistance to BRAF inhibitors [46].
Mutations in the JAK/STAT pathway have been found to play a role in the resistance to immunotherapy of melanoma. Pansky et al. [47] identified three different molecular alterations in the JAK/STAT pathway in melanoma cell lines, which could contribute to IFN resistance. However, Jackson et al. [48] casted doubt on this hypothesis suggesting that mechanisms leading to IFN resistance are heterogenous and do not only depend on mutations in the JAK/STAT pathway but also on components either downstream or additional to the JAK/STAT pathway. PD-1 blockage therapy play a valuable role in melanoma treatment and the JAK1/JAK2-STAT1/STAT2/STAT3-interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) axis was found to be crucial for the activation of the PD-1 ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2) [49]. According to Garcia-Diaz et al. [49], the regulation of PD-L1 is conducted mainly via IFN type II receptor signaling with the JAK1/JAK2-STAT1/STAT2/STAT3-IRF1 axis targeting PD-L1 promoter, whereas IFN-β and IFN-γ regulate PD-L2 through STAT3 and IRF1 transcription factors. In another study, epigallocatechin gallate, a green tea catechin, was found to inhibit melanoma growth by targeting JAK/STAT signaling and subsequently the PD-L1/PD-L2-PD1 axis [50]. Additionally, the ten-eleven translocation 2 protein (TET2) was found to mediate the IFN-γ/JAK/STAT signaling pathway and thus regulate chemokine and PD-L1 expression and cancer immunity [51]. Mutations in the genes encoding IFN-receptor–associated JAK1 or JAK2 were found to contribute to primary and acquired resistance to PD-1 therapy [52, 53]. Due to this fact, it has been hypothesized that oncolytic virus therapy can be an adequate therapeutic option in these types of tumors. Based on the study conducted by Nguyen et al. [54], oncolytic virus therapy can be used in the treatment of melanomas with IFN-γ-JAK-STAT pathway mutations, while the joint use of oncolytic viruses and JAK inhibitors is proposed to be used in melanomas without such defects.
The association between the mutations in JAK1, JAK2, STAT3 genes and the risk of developing melanoma as well as survival of the patients have been analyzed. According to the study conducted by Gomez et al. [55], single-nucleotide variants in JAK1 (c.1648+1272G>A, c.991-27C>T), JAK2 (c.-1132G>T), and STAT3 (c.*1671T>C, c.-1937C>G) alter the risk of cutaneous melanoma, whereas STAT3c.-1937C>G JAK1 c.991-27C>T has the most potent action, what can be related to the impact of STAT3 on the tumor cells proliferation and survival. In another study, the prognostic value of the JAK-STAT pathway gene expression was analyzed which showed that tissue samples with high expression of STAT1, STAT3, STAT4 and STAT5B, and low expression of STAT6 were associated with more favorable prognosis in cutaneous melanoma [56].
Non-melanoma skin cancer
Little is known about the role of the JAK/STAT pathway in the development and progression of NMSC. It has been demonstrated that ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor, inhibits cutaneous SCC cells proliferation in vitro by targeting the IL-22/JAK/STAT axis, which is activated in organ transplant recipients on cyclosporine A [57]. According to Chen et al. [58], B7-H4 and B7-H5 genes were under-expressed in cutaneous SCC lesions and regulated cancer development via the JAK-STAT and Notch signaling pathways. Moreover, abnormalities in the EGFR expression in cutaneous SCC may potentially serve a role in the proliferation and growth of the tumor, which is linked to the activation of PI3K/AKT and JAK-STAT pathways [59].
SAFETY OF JAK INHIBITORS IN CLINICAL AND OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES
Up to nowadays, multiple clinical trials have analyzed the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Upadacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, and tofacitinib, a JAK1 and JAK3 inhibitor, are approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with active psoriatic arthritis, while deucravacitinib, a TYK2 inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. The efficacy of tofacitinib in the treatment of plaque psoriasis was investigated in the OPT Pivotal 1, OPT Pivotal 2, OPT Retreatment, OPT Compare and OPT Extend studies. Nevertheless, the FDA approval was declined for the psoriasis indication based on safety concerns [60]. According to the recent meta-analysis which analyzed the risk of melanoma and NMSC in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with novel biologics (IL-12/23 inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors) and JAK inhibitors, the incidence rate (IR) of melanoma was 0.09 events per 100 patient-years (PYs) in patients treated with upadacitinib and tofacitinib, whereas the IR of NMSC was 0.7 events per 100 PYs [61]. These findings suggested that the risk of non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) may be modestly increased in patients treated with JAK inhibitors compared with those receiving biologic therapies, whereas the risk of melanoma appears comparable between the two groups [61]. Similar findings were presented by Olivera et al. [62]. In a systematic review and meta-analysis analyzing the safety profile of different JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, upadacitinib, filgotinib, and baricitinib) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel diseases, psoriasis, or ankylosing spondylitis, the IR of NMSC was 0.51 per 100 PYs, whereas the IR of NMSC in patients exposed to comparators was 0.27 per 100 PYs [62]. In meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials, extension studies and observational studies, an increased risk of various types of cancer has also been found in patients treated with JAK inhibitors compared to those treated with TNF-α inhibitors [63, 64]. According to a real-world cohort study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis treated with JAK inhibitors and TNF-α inhibitors, the risk of NMSC did not significantly vary between those two cohorts in patients with psoriatic arthritis, although there was an increased risk of NMSC in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with JAK inhibitors [65]. A study conducted by Jalles et al. [66], based on VigiBase®, the World Health Organization international database, found positive disproportionality signal for squamous cell carcinoma with ruxolitinib and tofacitinib, for melanoma with ruxolitinib and tofacitinib, for Merkel cell carcinoma with ruxolitinib and tofacitinib and only for Merkel cell carcinoma with baricitinib, indicating that there could be an association between JAK inhibitors and the risk of skin cancer. The safety of specific JAK inhibitors in terms of the risk of skin neoplasms has been assessed in clinical trials. OPAL Broaden, OPAL Beyond and OPAL Balance clinical trials investigated the efficacy and safety profile of tofacitinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis [67]. According to the studies comprising the total of 783 patients, none of them had melanoma, while 4 patients had NMSC [67]. In a pooled analysis of two clinical trials (SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2), upadacitinib was characterized by a similar safety profile: 3 events of melanoma and 14 events of NMSC occurred in the group of 1828 patients with psoriatic arthritis treated with upadacitinib at a dose of 15 mg or 30 mg daily [68]. The pooled results from the POETYK PSO-1, PSO-2 and long-term extension study demonstrated 11 events of NMSC and 2 events of melanoma in 1519 patients with psoriasis treated with deucravacitinib during the 2-year period [69]. Table 1 summarizes the key data and conclusions derived from clinical and observational studies.
Table 1
Summary of meta-analyses, clinical trials and observational studies evaluating the safety of JAK inhibitors with regard to the risk of skin malignancies
| Source | Study design | Disease | Study drug | Melanoma incidence | NMSC incidence | Summary of findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Krzysztofik et al., 2023 [61] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, open-label studies, long-term extension studies or observational studies | PSO, PSA | Upadacitinib, Tofacitinib | 0.09 events/100 PYs | 0.70 events/100 PYs | Patients treated with JAK inhibitors had similar IRs of melanoma and higher IRs of NMSC to those treated with biologics |
| Olivera et al., 2020 [62] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials (randomized or nonrandomized) and cohort studies (prospective or retrospective) | RA, IBD, PSA, AS | Tofacitinib, Upadacitinib, Filgotinib, Baricitinib | 0.51 events/100 PYs | The risk of NMSC was not increased in patients treated with JAK inhibitors compared with patients given placebo or active comparator | |
| Russe et al., 2023 [63] | Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and long-term extension studies | RA, PSA, PSO, axSpA, IBD, AD | Tofacitinib, Baricitinib, Upadacitinib, Filgotinib, Peficitinib | Increased risk of all malignancies including NMSC in patients receiving JAK inhibitors compared with TNF inhibitors. Incidence of all malignancies including NMSC was not significantly different between JAK inhibitors and placebo or methotrexate | ||
| Bezzio et al., 2023 [64] | Systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials and observational studies | RA, UC, CD, PSA, AS | Tofacitinib | Increased overall cancer risk was found in patients treated with tofacitinib compared to TNF inhibitors. The overall cancer risk was not increased when compared to placebo or biological drugs | ||
| Huss et al., 2023 [65] | Observational cohort study | RA, PSA | Baricitinib, Tofacitinib, Upadacitinib | RA: 59 events/1967 patients PSA: 8 events/379 patients | The overall risk for cancer other than NMSC was not significantly increased in patients receiving JAK inhibitors compared to TNF inhibitors; however, an increased risk for NMSC in patients with RA treated with JAK inhibitors was found | |
| Burmester et al., 2020 [67] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies with long-term extension (OPAL Broaden (NCT01877668), OPAL Beyond (NCT01882439), OPAL Balance (NCT01976364)) | PSA | Tofacitinib | 0 events/783 patients | 0.5 events/100 PYs (4 events/783 patients) | NMSC occurred in four patients in the tofacitinib comparison cohort, comprising two cases of basal cell carcinoma and two of squamous cell carcinoma |
| Burmester et al., 2022 [68] | Randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials (SELECT-PsA 1 (NCT03104400), SELECT-PsA 2 (NCT03104374)) | PSA | Upadacitinib | 15 mg: 2 events/907 patients 30 mg: 1 event 921 patients | 15 mg: 0.8 events/100 PYs (7 events/907 patients) 30 mg: 0.7 events/100 PYs (7 events/921 patients) | NMSC occurred in 14 patients receiving updacitinib, comprising 12 cases of basal cell carcinoma, 1 case of basosquamous carcinoma and 1 case of squamous cell carcinoma. Melanoma occured in 3 patients |
[i] NMSC – non-melanoma skin cancer, PSO – psoriasis, PSA – psoriatic arthritis, RA – rheumatoid arthritis, IBD – inflammatory bowel diseases, AS – ankylosing spondylitis, axSpA – axial spondyloarthritis, AD – atopic dermatitis, UC – ulcerative colitis, CD – Crohn’s disease, PYs – patient-years, JAK – Janus kinase, IR – incidence rate, TNF – tumor necrosis factor.
CONCLUSIONS
The JAK/STAT signaling pathway acts as a regulator of various cell processes such as cell division and apoptosis, playing therefore an important role in tumor formation and progression. In vitro studies demonstrated increased JAK/STAT signaling in both melanoma and NMSC and found that this pathway plays a role in the resistance of melanoma cells to immunotherapy. Clinical studies exhibit inconsistent findings regarding the risk of melanoma and NMSC in patients treated with JAK inhibitors indicating that there is a low or slightly elevated risk of skin neoplasms in this cohort of patients. However, further large-scale studies are needed to validate these findings, as currently data are conflicting and cannot serve as the basis for clinical decisions.







