Introduction
The State Emergency Medical Services (EMS) is an integrated emergency system that includes ground (ambulance) and air (helicopter) teams, hospital emergency departments (EDs) and trauma centers. Dispatches of outbound teams are carried out on the basis of an emergency 112 call and a decision made by a medical dispatcher. The Polish EMS system is established to save people’s health and lives; the teams intervene mainly to emergencies, the incident may occur in a private apartment, a public place, a workplace, a school, means of transport. Some of the interventions are in facilities providing institutional care for people with physical or mental disabilities, or who require care for other social and welfare reasons (loneliness, old age) [1,2].
There is an upward trend in demand for institutional care in Poland and other European Union (EU) countries. Life expectancy is increasing, and there are more elderly people in the community who require constant care due to diagnosed chronic diseases: cardiovascular, respiratory diseases, weakened skeletal system (osteoporosis), dementia (cognitive impairment), and impaired senses (vision and hearing) [3,4].
According to the World Health Organization, old age will be divided into several stages, namely:
60-75 years – early old age,
76-90 years – late old age (senile age),
over 90 years of age
longevity (advanced senile age) [5].
Population (demographic) aging affects Poland to a similar degree as other developed countries in the EU. Predictions by the Central Statistical Office show that in Poland in 2050 the share of people over 65 in the total population will be as high as 32.7% [6].
Neurodegenerative diseases, age-related dementia disorders, and mental impairments result in incapacity and dependence on care from family or appropriate facilities. Care for dependents should ensure that basic needs are met, including nutrition, hygiene provision, and assistance with medication [7,8].
In many cases, osteoporosis causes secondary disability in the elderly, which due to low-energy injuries (during daily functioning, a potentially harmless fall) results in permanent mobility disability [9,10].
In institutional care, there are two main types of care for people in need of support for various reasons, most often for social reasons, mental impairments, old age, neurodegenerative diseases requiring 24-hour care. A nursing care facility (NCF) provides comprehensive medical, nursing, rehabilitation care to people who require constant care (after surgery, after extensive injuries). In addition, the facility’s procedures include basic diagnostics. Another form of care is the residential care facility (RCF), which focuses on basic care, assistance with daily activities, and offers fewer medical procedures than the NCF [11].
Aim of the work
The aim of the work was the analysis and description of the Emergency Medical Service Teams’ (EMSTs) interventions to residents from nursing care facilities in 2021-2022.
Material and methods
Survey design
The study included a 2-year retrospective analysis of interventions by the EMSTs in the northern part of the Lublin Province, Poland (eastern border of the EU). The analysis covers period from January 1st, 2021 to December 31st, 2022. The data were obtained from the service records of the departing units of the EMS system:
departure order cards (DOCs) – this part is managed by the medical dispatcher at the Emergency Notification Centre (ENC),
Card of Medical Emergency Response (CMER) – completed by the manager (leader) of the EMST, namely: physician in the emergency medical system – specialized team (S), paramedic or nurse in the system – basic team (B) [1].
Four teams of 2 B-type and 2 S-type, 1 hospital ED in the district hospital are stationed 24/7 in the studied operating area, where the outbound teams transfer transported patients for further hospital treatment, observation, diagnosis. The patients who constitute the research population come from interventions from two types of facilities (categories of establishments) operating in the area:
1 nursing care facility,
5 different facilities with the following status: residential care facility.
Interventions meeting the inclusion criteria were analyzed, taking into account the date and time of the intervention, the duration of the intervention expressed in minutes, the location of the incident (urban and rural areas), the type of the EMST, the age and gender of the patient. Moreover, the study concerned rescue procedures, medical diagnoses according to the ICD-10 classification, use of pharmacological agents, the decision of the EMST as to whether to transport or leave the patient at the place of the call, and the destination of the patient’s transport. Interventions with patient deaths occurred in the analysis. Interventions were grouped according to the reason for the call with the following classification: behavioral disorders, cardiovascular disorders, neurological disorders, injuries, respiratory dysfunctions, metabolic disorders, infections, other (pain, allergies, cancer).
Statistical analysis
Results for quantitative variables are presented as mean values ± standard deviation. In a one-factor comparison of the characteristics of EMST interventions, a one-factorial Analysis of Variance (One-way ANOVA) was conducted. Qualitative variables (location, gender) were presented as quantitative values (n) and percentages of the total group (%), while proportions within groups were assessed using the Chi-square test. Statistica 13 software (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, OK) was used for statistical analysis. P<0.05 was taken as the level of significance.
Inclusion criteria
Calling the EMST to a resident residing in nursing and residential care facilities. The selection was made on the basis of the DOC of the area: the address of the location of the call and an additional description of the location of the call. Attention was paid to synonyms for the full names or abbreviations of care facilities, e.g.: “nursing home”, “NCF”, “seniors’ home”, “resident”, and addresses known to be locations of facilities providing care.
Interventions within the following dates: January 1st, 2021 0.00 am and December 31st, 2022 11.59 pm.
Patients residing in the designated facilities regardless of age.
Exclusion criteria
Patients receiving professional care (medical, nursing) in their own homes.
False calls (intentional or by mistake).
A call with the wrong location given – the EMST did not arrive at the location of the incident.
Call meeting the analysis criteria, but the team redirected to another, more urgent call by the medical dispatcher without arriving at the location of the incident.
Limitations
The obtained permission to access the data included only the records of outbound EMSTs, and no access was gained to records of further hospital treatment.
The use of pharmaceuticals described in the chapter titled ‘Results’ refers only to those drugs that were administered during the intervention from the supplies and equipment of the EMST. The authors did not have access to information on medications taken by patients on a regular basis.
Results
Using the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 177 EMST interventions were selected, representing 1.27% of the total medical interventions made in the operational area during the indicated two-year period (Table 1). In the analysis, there is a difference between the number of interventions and the patient population, which is due to repeated calls to the same patients, the results are presented in Table 2.
Table 1
General characteristics of the intervention
| Variable – year | Total number of incidents in the area | n included in the analysis | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 7 069 | 86 | 1.12 |
| 2022 | 6 769 | 91 | 1.34 |
| Total | 13 838 | 177 | 1.27 |
Table 2
Repeated interventions to the patient (data for n>2 interventions)
| Repeated | Gender/age * | Type of facility |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | M/44 | RCF |
| 3 | F/84 | RCF |
| 3 | F/89 | RCF |
| 2 | M/18 | RCF |
| 2 | M/52 | RCF |
| 2 | M/69 | RCF |
| 2 | M/70 | RCF |
| 2 | M/48 | RCF |
A total of 26 repeated interventions to 16 patients were carried out in the 2-year analysis, including 8 patients described in Table 2 and 6 patients with 1 repeated intervention. Significantly, 24 repeated interventions concerned facilities of the RCF type, and 2 of the NCF type.
In the analyzed group of subjects, it was shown that age had a statistically significant effect on the reason for calling the EMST (p<0.001). The highest mean age was for neurological disorders (77±18 years), while the lowest was for disorders of consciousness (44±18 years). No relationship was shown between the location of the patient’s residence (NCF vs. RCF) with reason for call (p=0.393), gender (p=0.279), type of facility (p=0.245), use of pharmacotherapy (p=0.524) and reason for call (p=0.813). The analysis showed that patients were transported most often to the ED (69% of cases), in 22% of interventions the patient stayed at the place of the call, and 9% (n=16) were transported to the emergency ward of a psychiatric hospital. Location of transport related to the reason for the call (p<0.001), where patients with pain complaints (pain of traumatic origin 95%, or in the course of aggravation of chronic disease 86% (Table 3).
Table 3
The general characteristics of the intervention of the EMST in the observed group
The use of pharmaceuticals (administered during interventions from the list of EMST drugs) concerned 44% of patients. This depended on the reason for the call (p=0.012), where 64% of patients with respiratory distress received pharmacological treatment during the EMST intervention. 146 (82.4%) interventions occurred to RCF (patient age min 18, max 94, mean 66.5, SD 21.7), and 39 interventions to NCF (patient age min 36, max 87, mean 67.7, SD 15.8). The age profile of the patients involved in the interventions varies widely, with 60 interventions for patients under 60 years of age, 36 interventions for the 60-75 age group, and 81 interventions for those >75 years of age. The majority of the EMST interventions were during daytime hours from 6 am to 7 pm (n=135), in the evening (7 pm to 10 pm, n=18), and at night from 10 pm to 6 am (n=24).
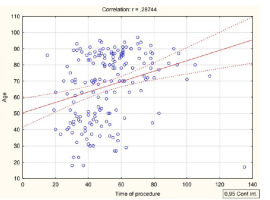
The reasons for the calls were also analyzed. There were statistically significant differences in the analysis of patient age and grouped cause of call and performed emergency medical activities (R=0.287; p<0.001) (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Age (in years) according to the reason for the call (according to the groups described in the Material and methods section)
The reasons for the calls were also analyzed. There were statistically significant differences in the analysis of patient age and grouped cause of call and performed emergency medical activities (R=0.287; p<0.001) (Figure 1).
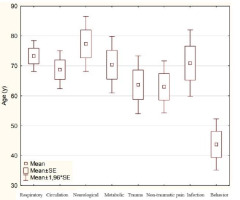
A comparative statistical analysis of 2021 vs. 2022 showed no statistically significant differences in intervention time (p=0.600) and resident/patient age (p=0.859) (Figure 2).
Medical diagnoses during the EMST intervention were analyzed according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) guidelines [12].
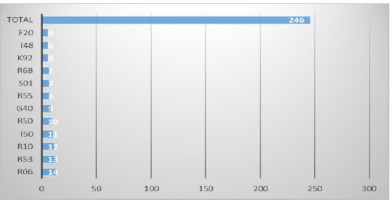
Figure 3 presents the most commonly used ICD-10 diagnoses. There were 246 diagnoses used in 177 interventions (mean 1.38/patient). With 69 interventions, 2 diagnoses were entered, mostly with trauma patients:
Figure 3
ICD-10 diagnoses for n>5
Notes: I10 – hypertension, R53 – malaise and fatigue, R10 – abdominal pain, R55 – fainting and collapse, R06 – respiratory distress, I50 – heart failure, I48 – atrial fibrillation and flutter, R68 – other general symptoms and signs, S01 – open wound of head, G40 – epilepsy, F20 – schizophrenia, K92.2 – gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
Discussion
The problem of disability, which is increasingly associated with the aging population of Europe, including Poland, is affecting an increasing number of people. In our own study, 60% of interventions concerned patients over 60 years of age [13].
A methodologically similar analysis was conducted by Zdzieborska et al. [14]. The authors studied the problem of mental disability in patients with limitations in intellectual functioning under institutional care requiring EMS. The type of team dispatched and the reason for the call were analyzed with respect to age, gender and medical procedures performed [14]. In our own analysis, there were also patients with intellectual limitations, but they were not a significant subgroup, and, what is interesting, they were younger in age.
Carron et al. [15] conducted an analysis of ambulance interventions in nursing residential care homes for people aged 65+ between 2004 and 2013. The period showed a linear increase in annual reporting frequency. The number of EMSTs interventions at nursing home residents increased by more than 200% during this period. Our own analysis, although covering a much shorter time period (2 years) also showed an upward trend in interventions related to the target of the analysis from 86 to 91 [15].
Warsz et al. [16] studied a Day Medical Care Home (DDOM), a nursing care and treatment institution designed for dependents, in which care is provided by a multidisciplinary treatment team. This type of care has been financed in Poland since 2015, and the authors describe the benefits of such an arrangement, taking into account data on geriatric wards in Polish hospitals (at the end of 2021, there were only 61 wards in Poland). The own research includes only patients from 24-hour care facilities. The authors have no information on further procedures and decisions for patients under study after transfer to the nearest ED. There is no department with a geriatric specialization in the studied area. All the EMST interventions occurred to 24-hour care facilities, of which only 24 (13.5%) occurred at night.
Ozga et al. [17], in a case study of a patient under the care of a British nursing home, describe the International Classification for Nursing Practice as a tool that enables nurses to standardize their professional practice in the realm of patient care. The own research, which was based on cards from EMST interventions, did not include scale and tools to assist in the nursing care of a resident in institutional care.
The analysis by Grant et al. [18] included transfers of patients from long-term care institutions to the ED, taking into account avoidable transports. Any preventable transfer exposes the patient to transport-related complications, and contributes to excessive emergency department occupancy, and increased costs for the health care system.
Czyżewski et al. [19], in a study of the EMST interventions to geriatric patients, showed on a group of patients (n=897) that during interventions pharmaceuticals were used most frequently for respiratory disorders (83%) and neurological disorders (47%, p<0.001). It also showed that patients whose call was due to neurological disorders were statistically more likely to be referred to the ED (76%, p<0.001). In our own study, transport to the ED was accomplished in 69% of cases, with cardiovascular patients being the main group.
A group of geriatric patients was observed by Celinski et al. [20]. This analysis focused on home interventions, but the results are similar to our own study once the disorder group is included as a reason for intervention. Cardiovascular diseases were diagnosed in 40% of patients, and 69.1% of the total ended in patient transport to the ED.
Timler et al. [21] also surveyed geriatric patient populations. The study included patients who were at least 65 years old (44% of all the EMST interventions), including 61% women, 39% men. As in other analyses and our own study, cardiovascular disease and trauma are the main reasons for calling the EMST in the study group.
In addition to the problem of disability in many patients whose families choose the care in professional establishments, loneliness is a social problem. The patient is in contact with many people (staff, other residents), but has no regular contact with his family. Women, people with primary education, rural residents, people on disability benefits, people with lower material status, and people from rural areas are significantly more at risk of loneliness [22]. The own research did not include a community interview with the patient regarding the reasons and causes for using institutional care.
Conclusions
Interventions due to circulatory and respiratory disorders dominate in the studied group. Transport to the hospital was necessary in the group of trauma patients, which is related to the lack of surgical procedures and the limited possibility of imaging diagnosis of the injury at the location of the call. The analysis includes a small number of incidents in relation to all interventions per year, which may be related to well-organized comprehensive care in public facilities, and high self-sufficiency in medical procedures (additional equipment, contracts with physicians – specialists, own sanitary transport). However, 69% of cases required transport to the ED, and 44% required the use of pharmacotherapy by the EMST.