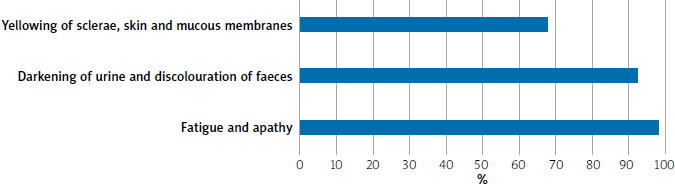Introduction
Chronic liver disease is one of the most common diseases in the world. It is especially difficult for patients with comorbidities. Even when taking medications, doctors always pay attention to toxicity and its effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, this problem is extremely important for research, especially today. The main research problem is the identification of new and analysis of old methods of treatment. After all, only by identifying the main mistakes of therapy can new, more effective ones be created.
This problem was analysed and investigated by Kayupov et al. [1], who determined that the most common causes are viral and alcoholic aetiological factors, as is widely acknowledged. The importance of the influence on the pro- and antioxidant systems in diagnostics and the influence of related factors on the recurrence of diseases were studied. The main symptoms and changes in the analyses of patients were determined, indicating liver disorders. Issues of regeneration during treatment were investigated by Kurakbayev et al. [2]. The authors paid attention to the restoration of liver cells in chronic lesions. The success of the therapy and its basic principles were analysed. They used the modelling method and explored the methods of therapy, and also pointed out the importance of correcting the condition of patients with the help of platelet-rich plasma. However, the authors paid little attention to treatment using biotechnological methods. The scientists analysed the results of therapy during the experiment and established the best methods of treatment for the subjects.
Deltsova et al. [3] examined the process of liver regeneration and explored the potential of using stem cells as a therapeutic approach for patients suffering from chronic liver diseases. Attention was paid to the histological basis of the structure of the gland and cell changes in various diseases. They also investigated methods to ensure the restoration of the liver without pathological processes. The authors paid more attention to anatomical features, but described the methods of therapy less. Sukowati and Tiribelli [4] noted that the method of liver transplantation is quite effective in cases of chronic diseases, but today the method of treatment using transplantation of stem cells of different origins is more effective. It was noted that at present there is still no definite single treatment protocol, so the study of this topic is extremely necessary.
Li et al. [5] investigated the main problems that doctors face in the treatment of chronic liver damage using biotechnological methods. The analysis influenced the progress of technology and changes in the use of stem cell therapy, as well as the results of doctors adding additional elements to the treatment. That gives greater efficiency and reduces the risk of secondary diseases and infection. Chronic liver damage occurs with factors of different aetiologies; therefore, at the first stages, the cause of the disease is established. The authors who studied this problem pointed out the importance of developing it and using new methods of treatment, which will provide a lower risk of relapse. It is important not only to analyse previous studies but also to identify the main principles that have already been proven. To reduce the population with already chronic liver diseases, it is necessary to study in more detail the intricacies of the application of biotechnological therapy, as pointed out by Lee and Suk [6]. To better understand the method of treatment and reduce morbidity, it is necessary to study this topic in more detail.
Aim
This study aimed to analyse the knowledge already available and to highlight new methods of using stem cells in treatment and the main complications during therapy.
Material and methods
A meta-analysis of existing studies was performed. Methods of analysis, comparison, generalization, and description were applied, and the main principles of stem cell therapy were identified. The study analysed the scientific literature from different sources. With the help of the analysis, the main aspects of the effectiveness of the method and its differences from others used previously, among them liver transplantation, were determined. The analysis makes it possible to delineate the positive and negative consequences for the body when using therapy. Using the comparison method, the risks of developing secondary diseases, and complications of various severity were studied. In the study of this topic, the indicators of these patients with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, were analysed. Comparative results of the experiments of scientists were evaluated. The influence of various aetiological factors, such as viruses and alcohol abuse, which are the main causes of diseases, was studied. The article used a comparison of the treatment at different stages of the disease and analysed the main risk factors for unsuccessful therapies.
Comparative analyses of patients of different ages and sex were performed; people from 20 to 40 years old make up 45%, from 40 to 60 years old 35% and patients aged 60 to 75 years old make up 20%. Of all those studied, men make up 57% and women 43%. The article highlighted the main symptoms of diseases and changes in blood counts, indicating the presence of a chronic form. Also, using the comparison method, differences in symptoms of various stages of diseases were determined and complaints of patients were analysed. The article examined the experiments of scientists from different years to determine the progress in the application of biotechnological methods of treatment and compared them with previously used methods. The analysis identified the most popular complications after treatment, as well as the likelihood of relapse. Positive and negative impact factors used in stem cell therapy were compared. With the help of a survey, the condition of 65 patients was analysed, and the main complaints and changes in the test results were identified, as well as complications that arose during stem cell therapy.
The article defined the basic principles of therapy and treatment of chronic liver diseases in people with different stages of the disease. The influence of concomitant diseases and their role in the occurrence of complications during treatment were determined. The main causes of diseases and the influence of the lifestyle of patients on the progress of the disease, as well as on the treatment and recovery of the body after the therapy, were analysed. The article summarized the available experimental results and the definition of the main provisions. The main principles of treatment were described and the main aspects of the effectiveness of the method were summarized. The study analysed the types of stem cells and methods of treatment with them. The main aspects of liver regeneration after the therapy were determined and the main factors that help accelerate tissue recovery were summarized.
Results
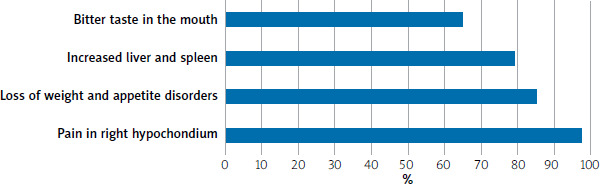
As Wang et al. [7] pointed out, chronic liver damage is one of the most complex and common diseases, affecting many people around the world. Its severity is reflected in severe complications and symptoms. The most common diseases are hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver. To prevent them, it is necessary to monitor lifestyle and nutrition at a young age, because the first causes of occurrence are viral infections and alcohol. Inactivity and non-compliance with the diet in the early stages of the disease complicate the treatment process. It is important to note that drugs are no less dangerous aetiological factor; their effect is harmful to the whole organism, but it is most toxic to liver cells. For the correct diagnosis of diseases, attention should be paid primarily to the complaints of patients, as Gao et al. [8] pointed out. During a study of patients diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver, it was found that 97% of people complained of pain in the right hypochondrium, 85% indicated weight loss and loss of appetite, and 79% of patients had an enlarged liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly). Patients with hepatosplenomegaly often reported a feeling of bitter taste in the mouth, especially in the morning (Figure 1). During the progression of the disease, the occurrence of ascites, dilatation of the veins in the abdomen, and jaundice and itching was noted. These symptoms suggest liver damage; for an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to use laboratory methods of research.
An equally dangerous liver disease is hepatitis, especially B and C forms, as noted by Kotkas et al. [9]. The main symptoms that occurred in patients include fatigue and apathy, which were reported by 89% of the patients surveyed. Characteristic symptoms by which hepatitis can be differentiated are darkening of urine and discolouration of faeces, 92% of patients encountered this, jaundice is also characteristic, characterized by yellowing of the sclera, skin and mucous membranes; 68% of patients encountered this symptom. Patients often experience digestive tract symptoms and elevated body temperature. The course of the disease depends on the type of virus. For a person, B and C are dangerous, since they can easily give rise to complications in the form of cirrhosis and liver failure. Joint pain also occurs (Figure 2).
The treatment of chronic diffuse liver lesions has undergone progress and new biotechnological methods have emerged. An older method of treatment is liver transplantation, but, unfortunately, the operation is quite dangerous, and in most cases, the organ is rejected. There is also a high probability of postoperative complications. Therefore, with the help of the latest technologies, new therapies have been developed, as mentioned by Riedel et al. [10]. One of the most promising methods is stem cell therapy. During the study, it was determined that this method is one of the most effective of all available today, but at the same time quite expensive. For the technique, stem cells of various origins are used. Primarily suitable for use in cell therapy is a mature hepatocyte, i.e. an already-formed liver cell; in case of damage to the organ involved in regeneration and transformation, there is a sufficient amount of them, and they are quickly activated after the liver damage. The second source of stem cells is an oval cell with active proliferating properties, as pointed out by Leshchuk et al. [11]. This type of cell is located in the canal of Hering, which is the final branch of the bile duct. These cells can transform not only into hepatocytes but also into other cells of the body. The third are bone marrow cells, which are available in small quantities and are rarely used in therapy. At the same time, they have a good ability to reproduce for a long time.
The study determined that stem cell treatments have two uses. The first is the transplantation of cells into the liver, after which they multiply and become hepatocytes. Thus, regeneration of damaged areas of the liver occurs and recovery is observed, as indicated by Zhang et al. [12]. The second application is the use of stem cells in the development of drugs administered to patients with chronic liver disease. This type of treatment is used when cell transplantation is not possible due to the presence of complications and concomitant diseases of various aetiologies. The study analysed the results of stem cell transplantation therapy at 6 and 12 months, using liver biopsy analysis. It was determined that in the absence of postoperative complications, the cells change and acquire the characteristics of hepatocytes, which regenerate the affected areas of the liver. It was determined that the treatment is quite effective, but expensive, which is why not all examined patients with cirrhosis or hepatitis were treated with this method.
However, it is important to note that the patients did not change their lifestyle and did not follow the diet for the necessary period for the body to recover, or did it partially and experienced a relapse of the disease, as reported by Carrera et al. [13]. To reduce the risk of secondary diseases during recovery, patients should strictly follow all medical recommendations and promptly contact their doctor at the first sign of relapse. An important element is dieting, because the liver directly affects the gastrointestinal tract, which makes it one of the main organs that prevents the toxicity of all substances entering the body, primarily alcohol. At the moment, stem cell treatment is not well studied and researched, so the occurrence of adverse reactions has not been determined. The main complications that can occur during treatment are infection, due to low immunity during therapy, reactions to anaesthesia and bleeding. In the event of their occurrence, the risk of mortality increases, as with other operations; therefore, before starting treatment, all minor deviations in the indicators in the analyses of patients should be noted. Also, a detailed diagnosis should be conducted and all potential complications should be analysed.
The study determined that stem cell therapy is more effective than liver transplantation therapy and symptomatic treatment. Cell transplantation therapy is not performed when the operation is not feasible and clear contraindications exist, for example, poor blood clotting, which leads to bleeding that is difficult to stop, as Fedulenkova et al. [14] noted. Thus, even with successful cell transplantation, the risk of mortality or deterioration in health becomes greater. To identify all the shortcomings of therapy, it is necessary to use it more often; then it will be possible to analyse all treatment errors and eliminate them in the future. However, because the procedure is not cheap, not all patients with chronic liver diseases can choose it for themselves. Therefore, the cases of its use in comparison with others are much rarer; therefore, it is difficult to eliminate all the shortcomings. The method is not well understood; however, the introduction of biotechnologies in medicine for the treatment of chronic diseases is a success for scientists and doctors.
The results of the study indicate the promise of this method, but the issue of its availability for all patients remains problematic. The number of patients with chronic liver diseases is constantly growing, which is influenced by various aetiological factors, so solving this problem with the help of stem cells is one of the most effective methods. Comparing the methods that were also used to treat diseases of the chronic form, it can be noted that the use of cells that subsequently change and acquire the characteristics of cells necessary for liver regeneration is one of the safest and most effective, as pointed out by Clària et al. [15]. Since there were many complications of liver transplantation, the body often rejected the transplant, and bleeding and infection occurred, which led to infection of the whole body and increased the number of deaths. Hence, even with a successful liver transplant, recovery was not fully guaranteed by doctors. Also, the method of symptomatic treatment, although the least risky and cheapest, unfortunately, is not fully effective, only providing some relief from symptoms for patients.
Research has shown that stem cells can be an effective treatment for chronic liver disease. They can help repair damaged liver tissue and prevent further progression of the disease. A meta-analysis analysed 9 studies investigating the effectiveness of stem cells in the treatment of chronic liver disease. Overall, the results of the studies have been encouraging, as stem cells are highly effective in the treatment of chronic liver disease. In particular, studies have shown that stem cells can help restore liver function and reduce the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. In addition, stem cells may be an effective treatment for hepatitis and other liver diseases. Therefore, taking into account the results of the study, it is possible to say that the use of stem cell transplantation in chronic liver diseases is an effective and promising method of treatment. This is indicated by the analyses of patients after a certain period, after recovery. The method does not cause numerous complications; therefore, it is safer for patients. Analysing the research data, it can be noted that out of 65 patients whose medical history was studied, they intended to carry out treatment with stem cells. Due to the low availability of treatment, 17 people refused therapy. Other patients were treated with stem cells, of whom 11 were allergic to anaesthesia medications, after which they were replaced. The results of the study indicate the feasibility of using the method and the prospects for its development in the future. The issue is not fully understood, but such treatment is used in many countries of the world, which indicates the prevalence of positive results of therapy. This encourages doctors to use this treatment method and to study the issues of complications as a result of its implementation.
Analysing the research data, it can be noted that serious and emergency complications have not yet been recorded, but it is imperative to conduct additional studies to prevent their occurrence. It is equally important to carry out treatment under the supervision of experienced medical specialists, and before starting treatment, undergo an examination by specialists of different specialties to determine possible contraindications or serious violations of the patient’s health. Before starting treatment, it is important to make sure that this particular method is appropriate in a particular situation, as well as to analyse the main problems that other specialists have and how to solve them to prevent them in patients in the future. It is also important to analyse effective operations, stages of implementation, main aspects and subsequent recovery of the body. The method is effective and efficient, but, unfortunately, has not been fully studied, so there is a risk of possible complications occurring in the long term following treatment. However, restoration of organ tissues using stem cells, subsequently directly involved in regeneration, is one of the most effective methods for treating chronic diffuse liver diseases. Therefore, the use of this method can be considered appropriate and effective.
Discussion
All research on the application of stem cells in treatment has been driven by the goal of reducing mortality in patients with chronic liver diseases. Upon analysing the drawbacks of current treatments, including organ transplantation and symptomatic therapy, scientists have found these methods to be suboptimal. Organ transplantation faces challenges such as donor shortages and the risk of organ rejection, while symptomatic therapy primarily addresses symptoms rather than the underlying cause. In light of these limitations, stem cell therapy has emerged as a more promising approach. Stem cells, which can be derived from various sources, possess the unique ability to differentiate into specialized cell types, offering a potential avenue for liver regeneration and functional restoration. This innovative method is currently under extensive investigation as a more effective strategy for treating chronic liver diseases.
Gao et al. [8] in their study, studied treatment with mesenchymal cells, and ways to improve therapy. The characteristics of patients with end-stage diseases and methods of their treatment were analysed. The authors concluded that the most dangerous consequence of not treating diseases is the potential to develop into liver fibrosis or even cancer. The scientists noted that the method of organ transplantation is one of the most effective, but it has many disadvantages, primarily the shortage of donors, postoperative complications, the high probability of immune rejection and the risk of infection, which is widely acknowledged. The authors conducted research based on the study of mesenchymal stem cells; they have good self-healing properties, and have the ability to differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells, thus increasing the chances of recovery.
Li et al. [5] investigated and described the main problems of therapy, as well as its progress. The scientists summarized the already available data on therapy and identified the main aspects. The authors considered various types of stem cell therapy. They also analysed the use of the largest source of cells, i.e. mesenchymal stem cells. Problems of therapeutic dosage, blood transfusion procedures and pharmacokinetics were determined. The scientists noted that the method is not completely studied, but has positive significant results, which makes it one of the most informative and open for research.
Zhang et al. [16] conducted studies to determine the effectiveness of the method for regeneration. The authors noted that the liver is one of the main organs influencing haemostasis and energy metabolism; therefore, a violation of its function leads to a violation of other systems. Therefore, it is the liver that is the first to experience the influence of toxic substances, as is widely acknowledged. In the study, scientists described the effectiveness of liver transplantation, but little was noted about the complications that arise during the operation. Although the method itself is effective, the conditions for this type of therapy must be ideal; otherwise, patients face many secondary diseases, which lead to deaths. The authors note that in recent years, stem cell transplantation has become a good alternative to liver transplantation. The study determined that hepatocytes and postnatal cells are appropriate to use, as they reduce liver damage and are quite effective.
Zhang et al. [17] conducted studies based on the study of stem cells isolated from the urine of patients with end-stage hospital-acquired liver diseases and their use in an experiment on mice. The authors note that urinary stem cells are differential and proliferative. Transplantation of such cells can partially restore the properties of a liver with chronic diseases. The authors determined that the use of urinary stem cells was a more effective method, so they conducted an experiment in mice, where the cells were isolated from urine samples of male patients with end-stage liver disease.
Liu and Yang [18] noted that chronic liver diseases are among the most common and dangerous. The authors analysed the properties of mesenchymal stem cells and determined that they are characterized by differentiation and paracrine effects and functions of antioxidant stress and immune regulation. Scientists noted that when using mesenchymal stem cells, they migrate to the affected liver tissue with the help of the blood circulation, where they act on the regeneration of the organ and alleviate damage with the help of the immune response. Scientists note that many researchers propose various methods of cell processing to increase their efficiency during transplantation.
Researchers from various fields of activity have determined the effectiveness of the treatment of chronic diffuse liver lesions using biotechnological methods, namely the use of stem cells. It was determined that today the technique is effective and safer, but not studied and expensive. Most researchers believe that the method of liver transplantation is effective, but it has many complications, so patients are faced with secondary diseases that occur during the operation. No significant complications have been reported during stem cell therapy. To prevent their occurrence, it is necessary to examine patients in detail, and contact specialists of various specialities to prevent the occurrence of even small negative consequences. It is also necessary to accurately verify the diagnosis and conduct a complete analysis of complaints indicating chronic forms of liver damage. To reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to consult the patient in time and indicate the main aspects of the recovery process, emphasising the maintenance of a healthy lifestyle and an appropriate diet for a certain time. It is important to diagnose patients who have undergone treatment after 6 and 12 months to make sure that the therapy is effective and that the patient complies with all the doctor’s requirements. Transplantation of different cell types is one of the main topics for research, since mesenchymal stem cells are most often used, due to their availability and abundance, but when using other types, a better result is possible. It is important to note that the cells used for this treatment must be differential and efficient. They are supposed to shrink affected areas of the liver by being converted into hepatocytes.
Thus, the chances of a full recovery are increased. The question of the availability of therapy for all patients remains problematic because, with frequent use of therapy, it is possible to improve it and exclude all possible complications. This will help ensure the effectiveness of the treatment. It is important to note that treatment is carried out in the case of chronic liver diseases, and to prevent them, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly at the slightest symptoms of liver dysfunction. The main aetiological factors in the occurrence of cirrhosis and hepatitis are frequent alcohol use, inactivity, an unhealthy lifestyle and viral infections. To prevent relapses after the treatment, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the doctor. After all, a disease of this nature, re-emerging, has severe complications and secondary diseases that often disrupt the activity of other body systems, which complicates the treatment process. The effectiveness of the method of treatment with stem cells is quite high, but not fully understood. However, the method is being extended and improved; it helps to analyse previous mistakes and avoid them in the future.
Conclusions
Cell therapy utilising embryonic, mononuclear, and mesenchymal stromal cells is a highly advanced and promising field in contemporary biotechnology and medicine, specifically for the treatment of chronic liver diseases. The capacity of stem cells to regulate disrupted intercellular interactions in the liver, influence mechanisms of cell death such as necrosis and apoptosis, and modulate fibrogenesis makes this approach particularly pertinent and promising in the field of hepatology. Although stem cell therapy holds significant potential, it remains a developing area that necessitates additional investigation and improvement. The efficacy of the treatment has been substantiated in numerous studies, wherein patients exhibited enhanced hepatic functionality and diminished disease progression.
Nevertheless, there are still obstacles that need to be addressed, such as enhancing the efficiency of cell delivery techniques, identifying the most suitable cell types and doses, and minimising potential hazards such as the formation of tumours. The current widespread clinical application of stem cell treatments is limited due to their high cost and limited availability. With the advancement of research and the refinement of techniques, there is an optimistic expectation that stem cell therapy will become increasingly available to patients afflicted with chronic liver conditions. Additional research is imperative to maximise the utilisation of stem cells, ascertain potential complications, and improve the affordability of this treatment. Although there are still obstacles to overcome, stem cell-based approaches are a substantial improvement compared to conventional treatments such as liver transplantation or purely symptomatic management.