Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (HP) is a Gram-negative and microaerophilic bacterium prevalent in more than half of the world’s population, particularly in developing countries [1]. HP infection is a significant public health concern, and its treatment remains challenging. The infection affects 24% of people in Oceania, 37% in North America, 47% in Europe, 55% in Asia, 63% in Latin America, and 79% in Africa [2–6]. Many upper gastrointestinal diseases, including gastric ulcers, cancer and lymphoma, are associated with HP infection [7, 8]. Successful eradication of HP can ameliorate gastric mucosal damage and prevent stomach cancer and other complications [9].
In the past, the standard triple therapeutic regimen consisting of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), amoxicillin and clarithromycin or metronidazole has been recommended as the first line choice for treatment of HP infection [10, 11]. Unfortunately, increased antibiotic resistance diminished the efficacy of the triple regimen [12]. The prevalence of resistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole, and levofloxacin was reported to be greater than 15%, so the efficacy of the standard triple regimen has diminished to fewer than 80% of cases over time [13–15]. Thus, using therapeutic regimens with high efficacy and minimal side effects, such as quadruple alternative regimens, is essential for HP eradication [16, 17]. Even though these treatment regimens can achieve acceptable eradication rates, the complexity and side effects of regimens containing multiple drugs may reduce patient compliance [18]. In addition, the use of four-drug regimens containing multiple antibiotics may result in multidrug resistance and, as a result, reduce the number of available effective antibiotics for alternative therapy in the event that eradication therapy fails [19, 20]. Therefore, effective therapeutic regimens with fewer drugs as an alternative option, particularly for elderly patients with several comorbidities, are necessary. Due to the antibiotic resistance of HP to many existing drugs, including clarithromycin, further research is required to determine the optimal first-line treatment regimen with the highest eradication rate and lowest side effects [21, 22]. In this regard, a combination of high-dose PPI and amoxicillin as dual therapy could be an effective therapeutic option for HP eradication [23–27]. To this end, the current multi-centric clinical trial was designed to compare the efficacy of the two-drug regimen of amoxicillin and pantoprazole with the quadruple clarithromycin-based regimen for eradicating HP infection.
Material and methods
The present study is a double blind, randomized clinical trial (RCT) on patients with confirmed HP infection referring to 8 medical centers in 3 countries (Iran, Egypt, and Vietnam) during the period October 2021 to March 2022. The study was performed after obtaining permission from the Research Council and approval of the Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (AJUMS) (IR.AJUMS.HGOLESTAN.REC.1400.098) and registration in the Clinical Trial Center of Iran (IRCT20211019052812N1, https://irct.ir/). Firstly, the purpose and method of conducting the study and the common side effects of the prescribed medication were explained to the patients. Then, eligible patients were included in the study if they wished, and were requested to sign a written consent form. In addition, at all stages of the study, provisions of the ethics statements of the Declaration of Helsinki and the principles of confidentiality of patients’ information were observed.
Inclusion criteria included patients aged over 18 years, clinical diagnosis of peptic ulcer disease (PUD), non-ulcer dyspepsia and or intestinal metaplasia based on a pathology report with confirmed HP infection, and no previous history of receiving HP infection treatment during the last year.
Exclusion criteria included patients aged less than 18 years and unwillingness to participate in the study, use of antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the last 4 weeks, history of allergy to any of the study protocol medications, history of gastric surgery or severe concomitant illness such as cancer, and pregnancy or lactation for women.
At the beginning of the study, patients’ essential characteristics, including age, sex, nationality, race, habitual history such as smoking and other concomitant comorbidities were collected and recorded based on a data collection questionnaire. After obtaining written consent, the patients participating in the study were randomly divided into two groups. The randomization method was based on random number allocation. In group A (high-dose dual regimen), the participants received amoxicillin 1000 mg and pantoprazole 40 mg every 8 h for 14 days and then pantoprazole at a dose of 40 mg every 12 h continued for 4 weeks. The subjects in group B (quadruple regimen) were treated with clarithromycin 500 mg, amoxicillin 1000 mg, bismuth sub citrate 240 mg and pantoprazole 40 mg every 12 h for 2 weeks, then pantoprazole at 40 mg every 12 h was continued for 4 weeks. The participants were in touch with responsible care given and requested to report any side effect leading to discontinuation of the medication by the patient.
Two weeks after the end of the treatment, a fecal HP antigen test was performed to prove the eradication of bacteria and the effectiveness of the treatment. The compliance of the participants was observed by assessment of the number of remaining medications. If the patient took the 14-day course of antibiotics thoroughly, it was considered as completion of the treatment.
Statistical analysis
The collected data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics software version 22 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). For quantitative variables, mean and median were used to describe central tendency, and interquartile range (IQR) was used to describe the spread of data between quartiles. Frequency and percentage were used to describe the data for qualitative variables. The normality of the data was evaluated by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, and the Levene test was used to evaluate the homogeneity of variance. The non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test and χ2 test were used to analyze the univariate data. Logistic regression and determination of the odds ratio at a 95% confidence interval were used for multivariate data analysis. The significance level for the tests was set at 0.05.
Results
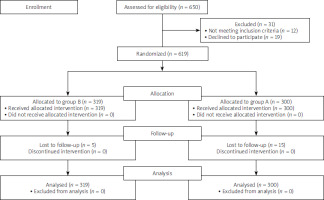
Overall, 619 patients with confirmed HP infection were included and randomly allocated to group A (high-dose dual regimen; 300 patients) and group B (clarithromycin-based quadruple regimen; 319 patients) (Figure 1). Patients included 259 (41.8%) men with mean age 44.3 ±14.11 years (range: 18 to 83 years). The baseline characteristics of the participants are presented in Table I. Causes of eradication include duodenal ulcer in 82 (13.1%) patients, non-ulcer dyspepsia in 462 (74.6%) patients, intestinal metaplasia in 36 (5.8%) patients, and gastric ulcer in 39 (6.3%) patients.
Table I
Baseline characteristics of participants; *χ2 test, **t-test.
The rate of HP eradication in ITT and PP analysis in group A and B were 68.3% & 72.2% vs. 85.6% & 89.9% respectively (p < 0.0001, Table II). Other variables such as age, gender, race, nationality, smoking, and cause of eradication had no significant effect on the rate of eradication (p > 0.05). The RR of side effects in the high-dose dual regimen was 0.548 (95% CI: 0.705–0.426,) compared to the clarithromycin-based quadruple regimen.
Table II
Comparison of eradication rates of HP infection and treatment compliance between two groups (*χ2 test, §from 299 patients, #from 195 patients, ¥from 319 patients, $from 284 patients)
In general, the most common side effects in group A include nausea and vomiting (8.7%), diarrhea (5.7%) and abdominal pain (3.3%), in comparison with bitter taste (18.8%) as the most observed side effect in group B (p < 0.0001). During the study period, the incidence rates of side effects in groups A and B were 66 (22.0%) and 128 (40.1%), respectively (p < 0.0001) (Table III).
Table III
Frequency of side effects in treatment groups (*χ2 test)
Non-adjusted analysis results showed that the success rate of the high-dose dual regimen (group A) was lower than that of group B (quadruple regimen) (OR = 0.38; 95% CI: 0.23–0.58, p < 0.0001). However, the dual regimen is associated with fewer side effects (OR = 2.37; 95% CI: 1.16–3.38, p < 0.0001). Nevertheless, the drug regimen had no significant effect on predicting adherence to treatment (OR = 1.19; 95% CI: 0.7–2.02, p = 0.501). In the modified logistic regression (adjusted analysis) based on various variables such as age, sex, race, nationality, diagnosis and cause of eradication and smoking, the two-drug regimen had a less successful eradication rate (p < 0.0001) and fewer side effects (p < 0.0001) but did not have a significant effect on predicting adherence (p = 0.57) (Table IV).
Table IV
Logistic regression to predict the effectiveness of two-drug regimen therapy (*adjusting for age, sex, race, nationality, smoking, diagnosis)
Discussion
According to the findings of the current study, the rates of HP eradication in the high-dose dual regimen of amoxicillin and PPI and the clarithromycin-based quadruple regimen group were 68.3% and 85.6%, respectively, based on ITT analysis, and 72.2% and 89.8%, respectively, based on PP, with a statistically significant difference. Consistent with the present study’s findings, the eradication rate with the high-dose dual regimen containing amoxicillin and PPI in the United States and South Korea did not demonstrate satisfactory results [28, 29]. In a study by Hu et al., the rate of eradication with the two-drug regimen in ITT and PP analyses was 78.1% and 79.1%, respectively, in comparison with 84.3% and 86.2% with the quadruple regimen. The incidence of side effects and drug compliance were comparable between the two groups [26].
In another study, Gao et al. compared the efficacy of a high-dose dual regimen and a four-drug regimen for eradicating HP. In the ITT and PP analyses, the eradication rate was 82.9% and 89.2% in the two-drug group and 86.1% and 93.9% in the four-drug group, respectively [30]. On the other hand, several studies have indicated that high-dose dual-drug regimens containing PPI and amoxicillin, if administered at the proper dosage and frequency, could be an effective method for eradicating HP infection [26, 31]. A study by Yang et al. demonstrated an eradication rate of 95.3% in the high-dose two-drug treatment group, 85.3% in the ten-day sequential treatment group, and 80.7% in the clarithromycin-based triple treatment group [31]. The efficacy of dual drug therapy was significantly superior to that of other regimens. There were no significant differences in drug side effects or treatment adherence in the study groups. The researchers concluded that the amoxicillin-based dual regimen was superior to the standard regimens for HP eradication, with the same tolerability and safety as the standard regimens.
Other studies that have also used a high-dose dual-drug regimen to eradicate HP infection have evidenced that the high-dose two-drug regimen exhibits the same efficacy and compliance as the quadruple regimen, with fewer side effects [25, 32, 33]. The meta-analysis by Yang et al. revealed that high-dose amoxicillin-based dual therapies and bismuth-based quadruple regimens for HP eradication had comparable efficacy (97.8% vs. 95.0%) and typically caused fewer side effects (14.4% vs. 11.4%) [31].
According to a recent meta-analysis by Xu et al., the two-drug regimen (high dose for 14 days) was reported as the optimal first-line treatment for HP eradication in the Asian population, with comparable efficacy and compliance along with fewer side effects than standard quadruple regimens. In the ITT analysis, the eradication rate for the two-drug treatment group was 91.7% vs. 86.7% for the four-drug regimen, and 95.7% vs. 92.0%, respectively, in the PP analysis. In addition, side effects were significantly lower in the group receiving a dual drug regimen in comparison with the four-drug regimen (9.6% vs. 23.0%). In a recent study conducted in China by Guan et al. (2022), the rate of HP eradication in the high-dose two-drug treatment group was 89.4% in the ITT analysis and 90.6% in the PP analysis, which was comparable to the eradication rate in the four-drug regimen group [32].
In a recent South Korean study, the rates of successful eradication with a four-drug treatment based on clarithromycin and bismuth as the first line of eradication treatment were 74% and 93%, respectively [34]. Multiple studies have reported a higher incidence of side effects in the clarithromycin and bismuth-based quadruple HP eradication regimen [32, 34]. For instance, a four-drug regimen consisting of clarithromycin, bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline was associated with a 61% side effect rate, according to one study. In contrast, 27% of patients in the amoxicillin and PPI treatment group experienced side effects. To overcome the challenges of antimicrobial resistance of HP and to reduce the effect on intestinal microbiota, it is necessary to identify appropriate and novel treatment regimens with a high eradication rate with minimal side effects. Although high-dose two-drug regimens containing a combination of antibiotics and PPI with different prescribed doses from the present study demonstrated acceptable eradication rates [23, 35], taking into account the promising results in using high-dose two-drug regimens evidenced in previous studies, additional research on optimizing high-dose two-drug regimens are recommended.
Although the current study was multicenter, with a large sample size, it also faced some limitations. It was not possible to match the two groups in terms of age and sex due to the multicenter design and high number of samples. Moreover, differences in race/ethnicity can affect bacterial resistance and the rate of eradication of HP infection. In the present study, there was no possibility of monitoring gastric pH and morphological changes of HP in patients’ stomachs during treatment, which may play a role in failure to achieve satisfactory effects of dual drug treatment [36]. It was also not possible to perform antibiotic susceptibility testing (especially for amoxicillin and clarithromycin) and evaluate the CYP2C19 polymorphism before starting treatment, which can help select the appropriate antibiotic and the optimal dose of PPI.
Conclusions
The present study revealed that a high-dose dual-drug treatment containing amoxicillin and PPI for treating HP infection was not associated with higher eradication rates than a clarithromycin-based quadruple regimen. Compared to the high-dose two-drug regimen, the four-drug regimen exhibited a higher eradication rate but more side effects and similar compliance. In order to eradicate HP infection, a four-drug regimen based on clarithromycin is still recommendable as first-line therapy.